About cookies on this site Our websites require some cookies to function properly (required). In addition, other cookies may be used with your consent to analyze site usage, improve the user experience and for advertising. For more information, please review your options. By visiting our website, you agree to our processing of information as described in IBM’sprivacy statement. To provide a smooth navigation, your cookie preferences will be shared across the IBM web domains listed here.
Article
Retrieval-augmented generation with LangChain and elasticsearch
Explore the use of elasticsearch for RAG to achieve a fast and efficient way of data retrieval and accurate response generation
When delving into the realm of generative AI, we see foundation models generating outputs that contain factual inaccuracies, or hallucinations, for various reasons. An effective way to improve the accuracy of generated output is to provide the needed facts as context in your prompt text. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) does precisely that, combining the foundation models with a knowledge base that is obtained from external retrievals. The idea is to enhance the capability of a generative model by allowing it to pull information from a vast corpus of documents during the generation process. This article explores the use of elasticsearch, a base class that is used to connect an elasticsearch database and to manage queries, for RAG to achieve a fast and efficient way of data retrieval and accurate response generation.
The retrieval-augmented generation pattern
The following image illustrates the RAG pattern. Although the diagram shows a question-answering example, the same workflow supports other use cases. See the Retrieval-augmented generation documentation for more information.
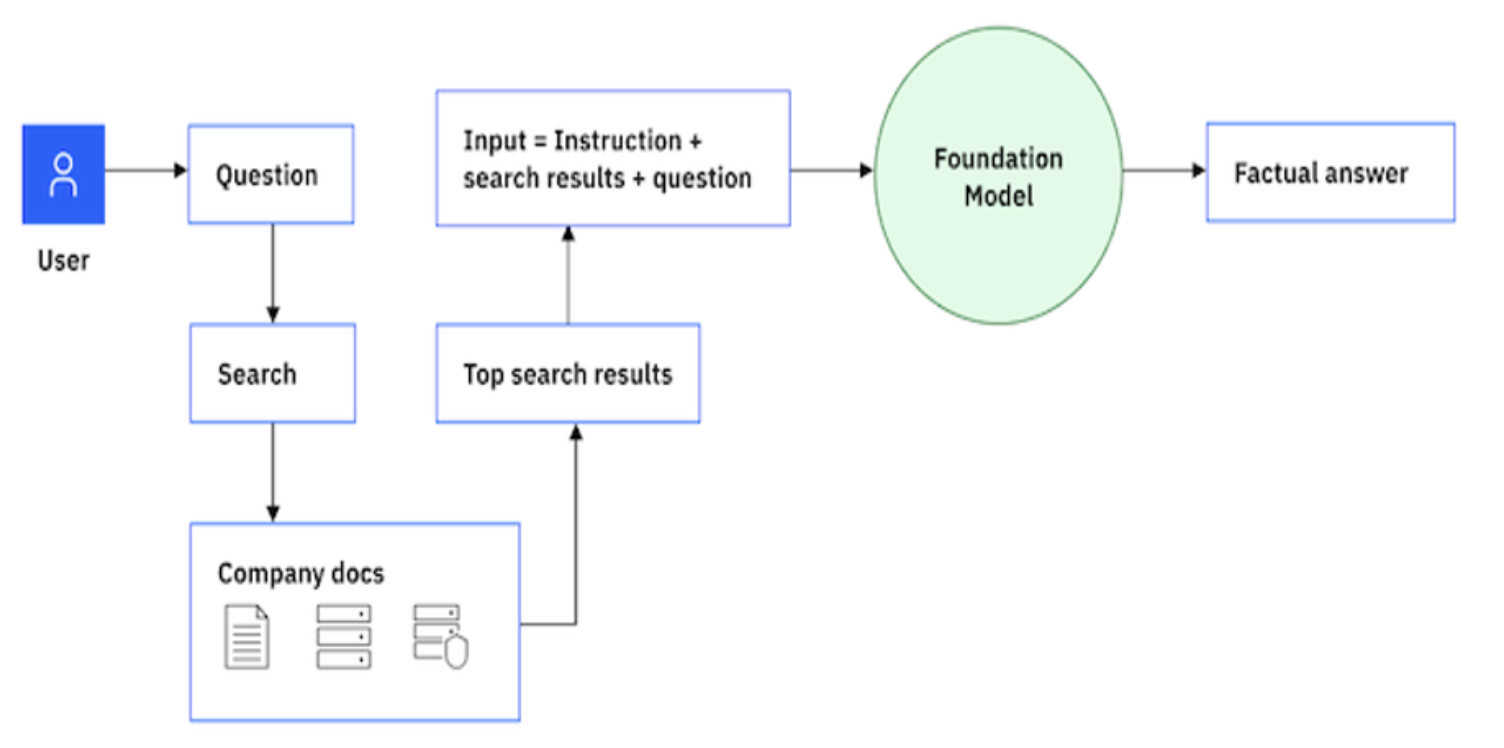
At a high level, retrieval augmented generation works in two steps: retrieval and generation.
- Retrieval: When presented with a question or prompt, the RAG model first retrieves a set of relevant documents or passages from a large corpus.
- Generation: The relevant passages that are retrieved are fed into a generative model along with the original query to generate a response.
Introduction to LangChain
LangChain is an open source framework that enables combining large language models (LLM) with other external components to develop LLM-powered applications. The goal of LangChain is to link powerful LLMs to an array of external data sources to create and reap the benefits of natural language processing (NLP) applications.
The LangChain framework consists of several parts.
- LangChain libraries: Python and JavaScript libraries that contain interfaces and integrations for a myriad of components, a basic run time for combining these components into chains and agents, and standard implementations of chains and agents.
- LangChain templates: A collection of easily deployable reference architectures for various tasks.
- LangServe: A library for deploying LangChain chains as a REST API.
- LangSmith: A developer platform that lets you debug, test, evaluate, and monitor chains that are built on any LLM framework and seamlessly integrate them with LangChain.
See the LangChain documentation for more information.
RAG with LangChain and elasticsearch: Learning with an example
elasticsearch is one of the most popular vector stores on LangChain. elasticsearch has production-ready vector database capabilities that you can use to build interesting use cases. Let's take a look at a detailed breakdown of the technical steps involved in RAG.
- Input query: The user provides a query that they want an answer to.
- Encoding: The input query is processed and encoded into a representation that the system can work with. This results in an encoded query. It's a representation of the original query that's ready for the retrieval process.
- Document retrieval: Using the encoded query, the system searches a large corpus of information to retrieve relevant documents or passages. This is done by using a dense retrieval method that is efficient and can fetch the most relevant pieces of information.
- Retrieved documents: The documents or passages that are retrieved by the system as most relevant to the encoded query that might contain potential answers or information requested.
- Context encoding: The retrieved documents are encoded into a representation that the system can work with, resulting in encoded documents.
- Combine encoded query + documents: The encoded query and the encoded documents are combined. This combination provides a rich context that the system uses to generate a final answer.
- Generation using LLM: Using the combined context from the previous step, a foundation model generates a coherent and relevant answer. It tries to provide the best possible response based on the information it has.
- Output (answer.): This is the final result. It's the answer or response that is generated by the system in reply to the original input query.
LangChain provides an abstraction for most of the steps that are listed previously, making it simple and easy to use. The following example shows how to achieve the previous steps by using LangChain capabilities.
Step 1. Load data
Load all of the documents and text in the form of vectors to build a knowledge corpus for the contextual search.
from langchain.vectorstores import elasticsearchStore
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import CharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
####### Load the document into elastic store using hugging face embeddings as the embedding function. Which could be one time activity depending on the use-case.
loader = TextLoader("./state_of_the_union.txt")
documents = loader.load()
text_splitter = CharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=0)
docs = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings()
db = elasticsearchStore.from_documents(
docs, embeddings, es_url="http://localhost:9200", index_name="test-basic",
)
db.client.indices.refresh(index="test-basic")
Step 2. Query data
Query the relevant documents to the sample input query, validating the vector database created.
### Here we are using to query the elastic search for the similarity based on the query that was placed. Which would return the results for the similar query.
query = "What did the president say about Ketanji Brown Jackson"
results = db.similarity_search(query)
Step 3. Automate the process
Use LangChain to automate the process of creating a vector passing and fetching the relevant documents, building the prompts on top of the question, and passing it to the LLM for the contextual answer.
### We could also leverage LangChain to further process the query and answer to our query by giving the elastic search vector search as retriever for the chain input.
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain.vectorstores import ElasticVectorSearch
db = ElasticVectorSearch(
elasticsearch_url="http://localhost:9200",
index_name="elastic-index",
embedding=embedding,
)
chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=model,
chain_type="stuff",
retriever=db.as_retriever(),
input_key="question")
chain.run(query)
This gives the final result. It's the answer or response that is generated by the system in reply to the original input query. This example outlines how you can use LangChain and elasticsearch to achieve a simple, fast, and efficient way of data retrieval and accurate response generation with LLM.
Next steps
Want to learn more about retrieval-augmented generation? Then take a look at a few other IBM Developer articles such as Retrieval-augmented generation with large language models from watsonx.ai and Implement generative AI in intelligent workflow automation with the IBM watsonx platform.