Article
Introduction to data fabric
Learn about data fabric architectures, and get an overview of the IBM data fabric approach
To be competitive, organizations use data as a differentiator, and there is a need to create differentiated experiences for all stakeholders. Each department within an enterprise, such as sales, marketing, operations, HR, or IT, uses the data to derive insights and to get a competitive edge.
Data challenges
In a hybrid multicloud environment, enterprises face the challenge of siloed data, which can be intensified by the ever-increasing volumes of data. As data sources multiply and generate vast amounts of information, the sheer volume becomes overwhelming for traditional data management approaches. Siloed data exacerbates this issue, making it even more challenging to handle the expanding data volumes effectively. For most enterprises today, operational data has largely remained siloed and hidden, leading to an enormous amount of dark data. As a result, most organizations consider their data unreliable.
Some of the data challenges that enterprises face include:
- Increasing data volumes
- Multiple locations, clouds, applications, and data silos
- Complex data formats, including documents, images, and video
- Data quality issues
Efforts to centralize all data rarely succeed because a mixture of on-premises and multicloud environments make it a complicated process. Clouds and cloud data warehouses add to the complexity. Then, there is an increasing need for regulatory compliance, security, and addressing governance risks. All of this makes discovering all of the data more challenging.
Implementing data governance, data integration, and consolidation strategies across multiple cloud platforms becomes vital to ensure efficient data management and analysis. Data insights can be achieved with data science, MLOps, and AI governance. Ultimately, the goal is to connect the right data at the right time to the right people from anywhere rather than collecting all of the data in one place or connecting each data source or application to one another.
This opens the door to a new approach: using a data fabric. A data fabric is a data architecture with an integrated set of technologies and services that are designed to democratize data access across the enterprise at scale. By addressing both data silos and the exponential growth in data volumes with the data fabric, enterprises can capitalize on the insights and opportunities that are presented by their multicloud environments, while maintaining a secure and compliant data governance strategy.
IBM Cloud Pak for Data is the solution IBM uses to implement the data fabric. It is an integrated data and AI platform that enables organizations to collect, organize, analyze, and infuse AI capabilities with their data. It provides a unified and scalable environment for different roles like data engineers, data scientists, business analysts, data stewards, and administrators to collaborate and derive insights from data. IBM Cloud Pak for Data offers a range of tools and services, including data integration, data governance, data quality, data cataloging, machine learning, and analytics, all built on an open architecture. It aims to accelerate data-driven decision-making and help organizations use their data assets effectively.
The data fabric is a balance between what needs to be logically or physically decentralized and what must be centralized. For example, within an enterprise, each department can maintain their own catalog, but these department catalogs can be augmented with an enterprise-level catalog that defines the over-arching global governance. A data fabric is not a single product or a single technology. It's an emerging data management concept and architecture, which through utilization of advanced technology accelerates data delivery and access to data.
There are certain characteristics that a data fabric architecture must have to achieve data management.
- The data fabric is not a set of point-to-point connections or a single hub-style data collection. It logically spans across disparate and hybrid data sources. This virtual net is established through an intelligent AI-driven knowledge catalog.
- There is metadata that is generated around how data is linked. It needs to enable users to understand the data for business use and to derive insights.
- The metadata in a data fabric differs from previous metadata catalogs that were only dictionaries to better understand the data. The data fabric metadata is used to drive automatic decision-making with metadata activation.
- The data fabric provides automation on how data is delivered and ensures that the right data is available to the consumer based on their role.
- The data fabric provides for a “shop for information” experience by providing a holistic view of the information. The knowledge catalog is the brain that controls and orchestrates data consumption.
- The catalog uses AI to be highly automated. Data discovery and cataloging of data sources is automated. You need to make a connection only to the data sources, then assets can be mapped, and semantic enrichment added to make the data available for further use. Human intervention can be limited to reviewing the metadata enrichment and moderating the process.
- A data fabric helps toward creating data integration pipelines, services, and semantics in support of various operational and analytics use cases. These can be delivered across multiple deployment and orchestration platforms.
- Data fabrics support a combination of different data integration styles and use active metadata, knowledge graphs, semantics, and machine learning to augment (and in some cases completely automate) various data integration design and delivery tasks.
- This might not seem like a new concept, but a modern data fabric approach lets you enable decentralization so that you can scale data access across your company.
Why data fabric is becoming important
The key drivers include the following:
- Cloud adoption with data on multiple clouds, data centers, on premises, or edge locations
- Large volumes of data generation: structured, semi-structured, and unstructured
- Self-service analytics requirements
- Automation in data management and data integration
- Supply chain data resides across the organizations varied data sources
The IBM data fabric architecture
The IBM data fabric is an architectural approach to simplify data access and facilitate self-service analytics for insights. A data fabric includes the appropriate controls to support the required data flows, processes, and consumers of that data within an organization. By using this architecture, it becomes easier to integrate with data pipelines and new on-premises and public cloud environments using the power of AI and automation.
The data fabric primarily derives value from the federated active metadata. Metadata is defined as data that describes data. The data fabric helps stitch together the data silos and data fragmentation using the metadata.
Through its comprehensive capabilities, a data fabric ensures seamless integration, accessibility, and governance of data from diverse sources, enabling business users, data scientists, data engineers, and data analysts to effectively use data. It facilitates large-scale innovation, particularly in AI, by providing controlled data sets for AI applications.
Data fabric: An architectural approach to simplifying access to data
The following image shows the data-driven strategy for enterprises with IBM data and AI.
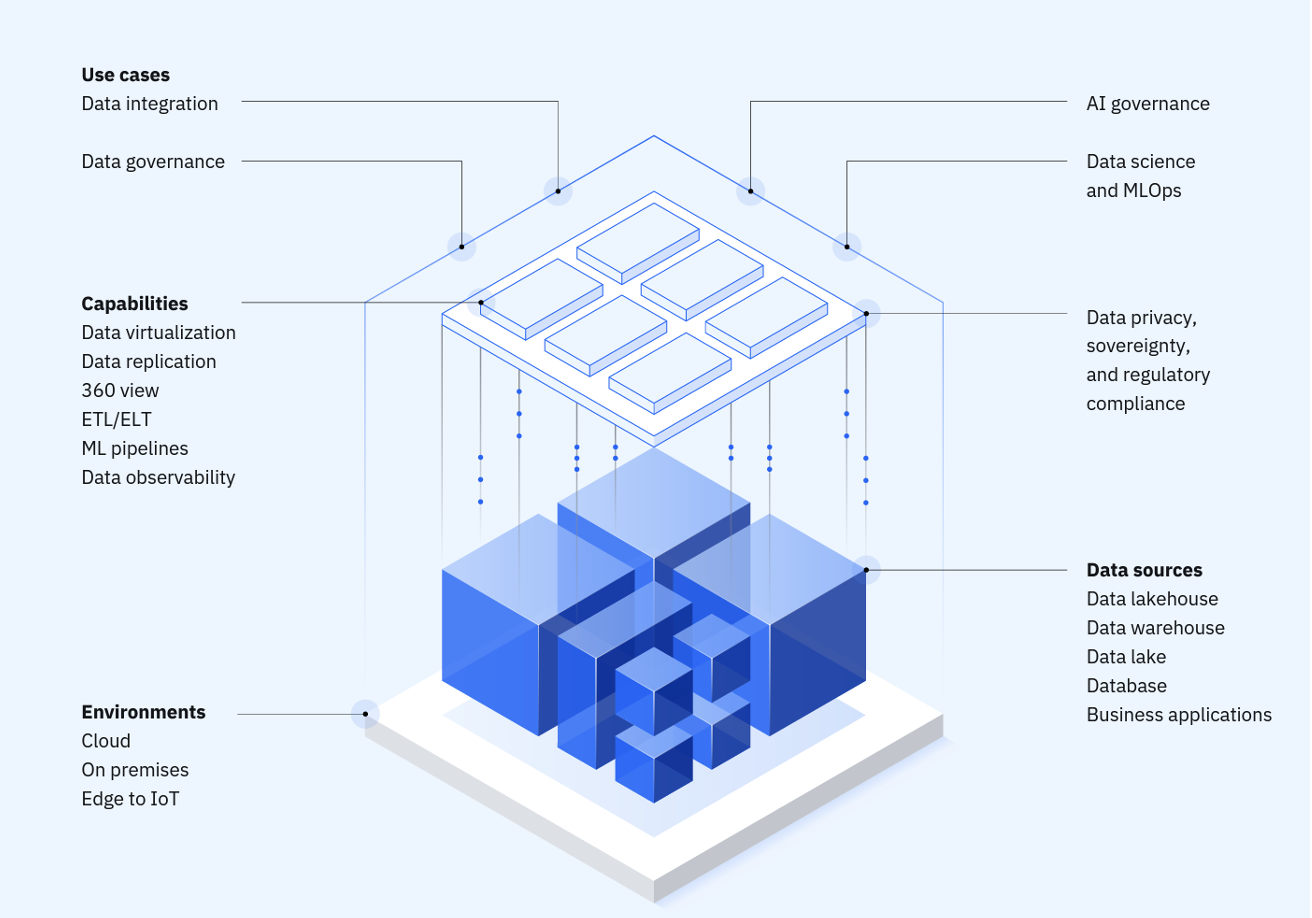
The following image shows the end-to-end capabilities, integrations across the entire stack, and the ability to provide solutions in various domains.
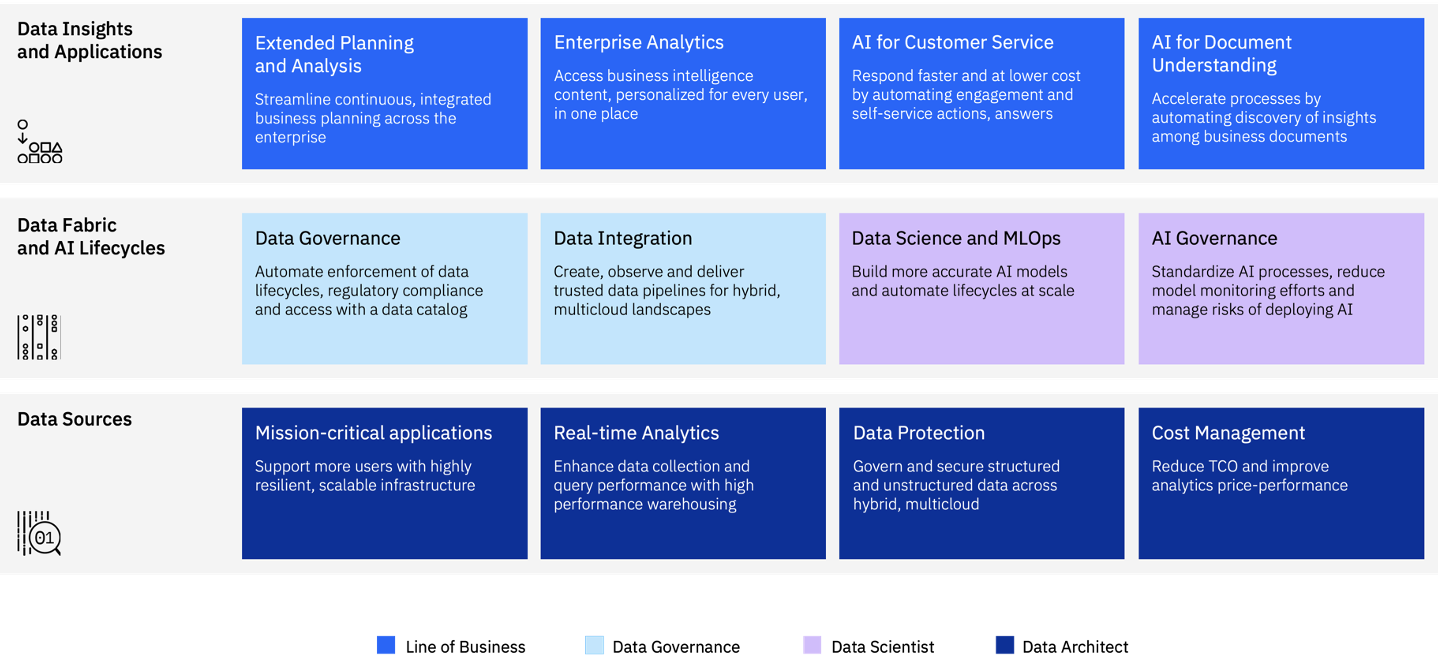
Key pillars of a data fabric
Data governance
Data governance helps manage data effectively and securely throughout its lifecycle. It ensures data accuracy, consistency, and compliance while mitigating risks. By implementing data governance, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data assets, enhance decision-making processes, and gain a competitive edge in the data-driven world.
Data governance enables organizations to create a trusted and protected business-ready data foundation. It addresses:
Knowing your data and establishing data governance: To set up the foundation of a governance program, organizations must comply with regulatory requirements, share business concepts and definitions, communicate and enforce policies and standards, and identify classifications and ownership. IBM Knowledge Catalog helps manage business, technical, and operational metadata, and also generates knowledge graphs that help you uncover the relationships between the data. Automated metadata curation services like auto discovery and classification of data, knowledge accelerators, and auto assignment of business terms from a business glossary helps better understand the existing data.
Trusting you data: Providing easy access to quality data is important if proper insights are required. With data profiling with IBM Knowledge Catalog, you can achieve data quality scores based on the different data quality dimensions like accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Data lineage services for data at rest with Manta as well as data in motion with Databand helps bring in traceability between sources and targets across the data pipelines that results in better trust and explainability and helps reduce operational costs.
Protecting your data: Autonomous enforcement of data and AI governance policies. As active data is made available to more data consumers for self-service access, sensitive data must be dynamically protected and masked to ensure data privacy. Rules and policies can be set up for data privacy, enforcing regulatory compliance like General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPPA), or data sovereignty. IBM Cloud Pak for Data also provides a workflow to manage data based on different roles that enables fine-grained control on data access across the enterprise.
Using your data: Enabling self-service access to trusted data. The dependency on the IT department is reduced as people in various roles (for example, business analysts) can generate reports or derive insights from the organization's data based on the metadata enrichment. They can search and discover relevant data, perform tagging and annotations, or add comments. Workflows can be defined so that based on the role, different users can manage the data governance. Data stewards, data engineers, data scientists, and business analysts can collaborate on the platform for self-service analytics.
Data integration
There is a need to deliver readily consumable and reliable data to your teams anytime and anywhere. In situations where there is a question regarding data reliability, the data fabric architecture should be able to detect, explain, and quickly remediate data reliability issues.
Data integration enables organizations to simplify access to decentralized data, including:
Democratize access of enterprise data across a decentralized hybrid cloud landscape. Because enterprise data can reside on-premises or across multiple clouds, there is a need to be able to access data across heterogeneous sources with minimal data duplication to minimize costs and defects arising out of data getting out of sync across different copies of data. Watson Query is a universal data access layer that automates how you access and unify data across any source or type (clouds, warehouses, or lakes) with data virtualization, without the need for data movement or replication. You can have one query experience over multiple data sources, types, and form factors. Its open data formats work with data on any cloud and on-premises, and its intelligent cache recommendations accelerate query performance with minimal user input.
Ability to transform and integrate the data to collect the data in a required format. Often, it's not possible to derive insights from the data without transforming or standardizing the data coming from across different sources. There can be multiple systems of records that might provide inputs, and this data must be integrated into a hybrid, multicloud environment. With Data Refinery on IBM Cloud Pak for Data, non-IT personnel can perform lightweight transformations on the data and do the visualizations. The Data Refinery service reduces the amount of time that it takes to prepare data. You can use its predefined operations in your data flows to transform large amounts of raw data into consumable, quality data that’s ready for analysis.
If Data Refinery is not adequate, you can use IBM DataStage to compose your data flows with speed and accuracy by using its intuitive graphical design interface to connect to a wide range of data sources, integrate and transform data, and deliver the data to your target system in batch or real time. The tool offers a design once, run anywhere paradigm with support for dynamic invocation and elastic scaling. It also provides remote job execution to minimize cloud egress costs by taking the processing to your data that might potentially reside anywhere. Similarly, the change data capture (CDC) engine helps in mirroring data from different source systems to target systems to achieve data integration. Various data integration patterns are possible with IBM tools that provide tight integration into complete data fabric elements, and providing high scalability at the same time.
Data observability
Data observability is the end-to-end monitoring of the data health across the enterprise. It provides the ability to have a broad visibility of its data landscape and multilayer data dependencies (like data pipelines, data infrastructure, and data applications) at all times. Operational alerting, response, and remediation is possible with IBM Databand from an operations perspective. The mean time to detect a failure (MTTF) or the mean time to recover (MTTR) from a failure is reduced across the data pipeline. Manta with Watson Knowledge Catalog provides for data observability in design time with data lineage for both business and technical metadata.
Data science and MLOps
With data science and MLOps, the MLOps lifecycle management is simplified. MLOps is provided through Watson Pipelines along with Watson Studio and other services for AI on IBM Cloud Pak for Data. Uncontrolled AI is a threat to organizations. It can result in damage to the brand, regulatory noncompliance, and even lost revenue or higher expenses if the AI provides bad results. Organizations cannot easily deploy models, or there can be barriers to their use. AI models require continuous monitoring and refreshing with new data as conditions change. There can be drift and bias in models.
IBM’s approach is all about operationalizing AI, and the approach addresses the need for MLOps with trust that is instilled throughout the entire AI lifecycle. The approach:
- Ensures that the right data is available at the right time with the right governance during the data collection, organization, and preparation processes.
- Accelerates the time that it takes to get models into production, and monitors and ensures that the models are fair during model building, deploying, validating, and monitoring.
- Creates a process that is built on automation and consistently applies model governance throughout the entire AI lifecycle, from data collection to model building and production.
AI governance
AI governance is managing production AI with trust and confidence in outcomes. The data fabric helps enable organizations to operationalize AI with governed data. It ensures that your data is accurate, consistent, timely, and complete. It allows stakeholders to collaborate in an access-managed environment with industry standard tools. It captures model metadata automatically, and helps manage AI risk across the organization. AI governance also is monitoring models for bias and explainability, and meeting or exceeding AI regulations. For this, data is captured across all stages of the AI lifecycle. Through Python notebooks, it's possible to automate metadata and data transformation and lineage capture.
For example, models are created or imported into Watson Studio, followed by metadata discovery and enrichment. IBM OpenScale helps with AI observability. The business, technical, and operational metadata and knowledge graphs are managed by Watson Knowledge Catalog. Watson Knowledge Catalog also is used for enforcing policies and rules to implement data privacy, sovereignty, and enforcement of regulations. Models can be deployed on different public clouds with model risk management workflows that are managed in IBM OpenPages. IBM OpenPages does model risk management workflows.
The key capabilities of IBM OpenPages include:
- Deployment flexibility: Monitor models that are developed in Watson Studio or any IDE or open source framework and hosted in Watson Machine Learning or any third-party or private model serve engine.
- Model fairness: Detect and automatically mitigate bias at both build and run time to ensure fair outcomes.
- Explainability: Explore the factors that influenced an AI outcome in easy-to-understand business terms. Understand how changing factors would produce improved outcomes through contrasting explanations.
- Model Ops: Script or configure models into application deployment pipelines to enable actions on models, including start, stop, and redeploy.
Conclusion
This article describes the IBM data fabric approach, which offers autonomous enforcement of policies and controls through automated governance, protection, and security. The data fabric architecture enables uniform policy enforcement across the enterprise, supporting data privacy and sovereignty policies. It includes end-to-end automation with core features, such as AI-powered data discovery and automated data protection policy enforcement.
The approach allows organizations to leave data where it resides, supporting various data integration methods. It provides an automated framework that governs the development, deployment, and operation of AI systems to ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability. This comprehensive solution helps improve productivity, reduce costs, ensure compliance, and address historically manual data operations with automation at scale.