About cookies on this site Our websites require some cookies to function properly (required). In addition, other cookies may be used with your consent to analyze site usage, improve the user experience and for advertising. For more information, please review your options. By visiting our website, you agree to our processing of information as described in IBM’sprivacy statement. To provide a smooth navigation, your cookie preferences will be shared across the IBM web domains listed here.
Article
Build a multilingual language detection and translation system using IBM watsonx.ai
Pretrained LLMs help you quickly develop an intelligent language system
IBM watsonx.ai simplifies the process of building AI-powered solutions. For example, with just a few lines of code, we can leverage its models to identify languages and generate accurate translations. A system can easily be integrated into applications like customer support, content localization, or even personal language-learning tools.
In this article, we’ll explore how to use watsonx.ai to build a multilingual language detection and translation system. With watsonx.ai's pretrained AI models, it's simple to develop intelligent systems without starting from scratch.
To get a closer look at watsonx.ai capabilities, we’ll create a system that detects languages and translates text. We’ll build an LLM-powered system that can detect and translate languages, making the system smarter, faster, and more reliable.
Let’s dive into how we can create this system step by step. And don't worry, we'll keep things simple and easy to follow.
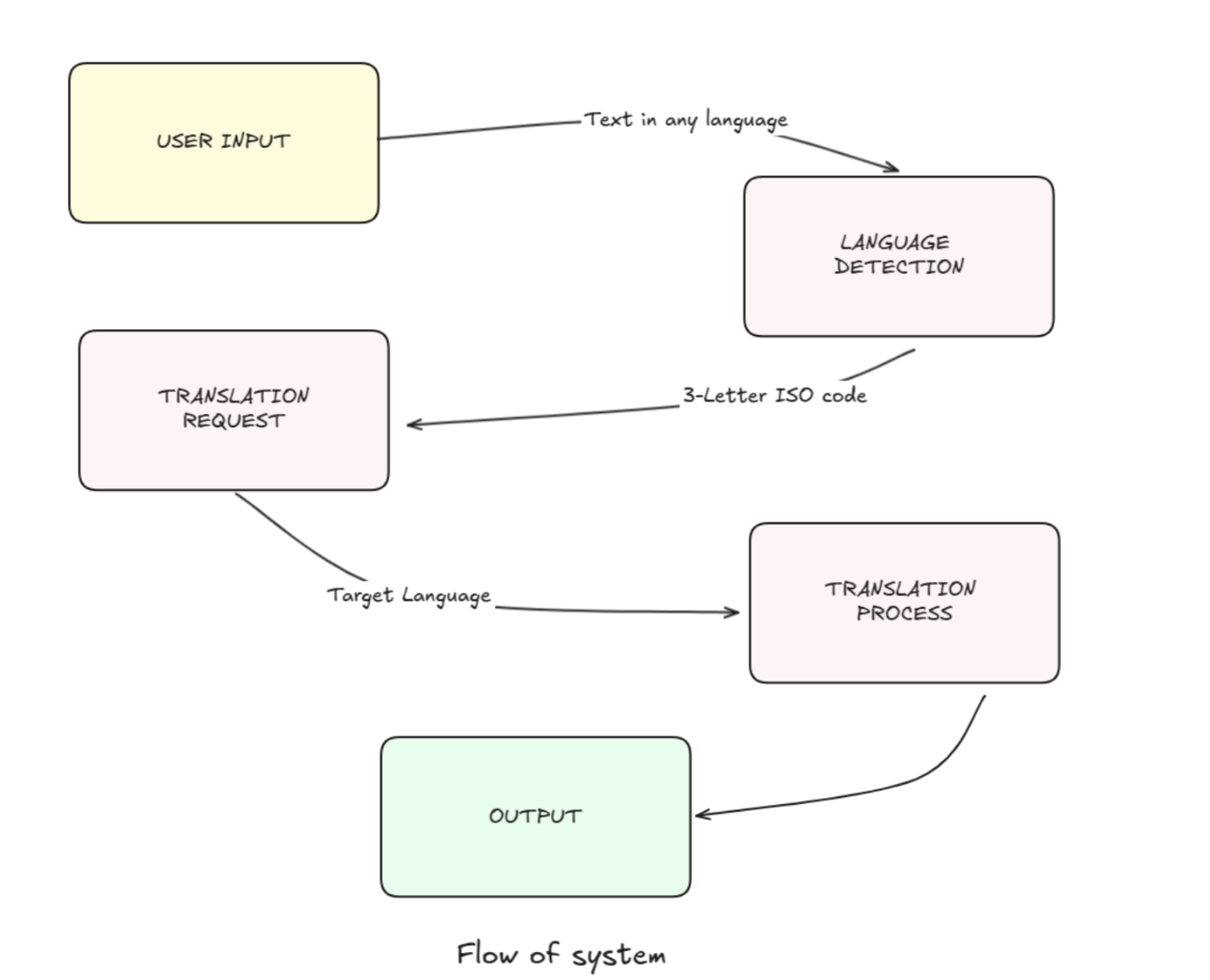
System overview
The system we're building has two main components:
- Language detection: Given a piece of text, the system will identify the language it's written in and return the corresponding 3-letter ISO language code.
- Language translation: The system will translate text from one language to another, following specific instructions to ensure accurate and contextually appropriate translations.
Ideal for accomplishing our goal, watsonx.ai provides pre-trained models for various natural language processing tasks, including language detection and translation.
Before you begin
To get started, you’ll need to set up a watsonx.ai project to gain access to the watsonx LLMs for data generation. Complete the following steps:
- Login to watsonx.ai using your IBM Cloud account.
- Create a watsonx.ai project.
- Create a Watson Machine Learning service instance (choose the Lite plan, which is a free instance).
- Generate an API Key in WML.
- Associate the WML service with the project you created in watsonx.ai.
Set up the environment
Before diving into the code, we need to set up our environment. This involves installing the necessary libraries and configuring the watsonx.ai API key.
We need to import the WatsonxLLM class from the langchain_ibm library, which allows us to interact with watsonx.ai models. We also set the WATSONX_APIKEY environment variable to our IBM Cloud API key.
Run the following:
from langchain_ibm import WatsonxLLM
import os
os.environ["WATSONX_APIKEY"] = 'YOUR API KEY'
Configure language detection
The first component of our system is language detection. We'll use a prompt-based approach to instruct the model to identify the language of a given text and return the corresponding ISO code.
Prompt design: The prompt is designed to guide the model in identifying the language and returning the correct ISO code. Here's the prompt we'll use:
lang_detection_prompt = '''
{header}
<system>
You are an expert in detecting languages. From the input provided identify the language and share the 3 letter ISO code for the same.
Reference:
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) creates standardized language codes to represent languages and language groups.
These codes are used internationally to identify languages in various contexts.
Example - 3 letter ISO for 5 languages
1. English: eng
2. French: fra
3. Spanish: spa
4. German: deu
5. Chinese: zho
6. Hindi: hin
Instructions:
1. Identify the language from the input given below
2. Respond with the language and the ISO code of the language
3. Don't respond with anything else, just the language and the ISO code. No header/footer/code etc.
4. Follow the 4 examples shared below and based on that answer the last one.
5. Follow only the instructions between the tags <system> and </system>
Examples:
Input: The secret of getting ahead is getting started!
Output: English - eng
Input: मैं कभी हारता नहीं हूँ। मैं या तो जीतता हूँ या सीखता हूँ।
Output: Hindi - hin
Input: La gloire d’hier ne garantit jamais le succès de demain.
Output: French - fra
Input: 一生懸命働けば働くほど幸運になることがわかりました。
Output: Japanese - jpn
Input: {input}
Output:
</system>
{footer}'''
This prompt provides clear instructions and examples to help the model accurately detect the language and return the ISO code.
Generate the response
To generate the response, we'll use the generate_response function, which interacts with the watsonx.ai model:
def generate_response(prompt, model):
parameters = {
"decoding_method": "sample",
"min_new_tokens": 1,
"max_new_tokens": 4096,
"stop_sequences": [],
"repetition_penalty": 1,
'temperature': 0.5
}
watsonx_llm = WatsonxLLM(
model_id=model,
url="https://us-south.ml.cloud.ibm.com",
project_id='YOUR PROJECT ID',
params=parameters
)
response = watsonx_llm.invoke(prompt)
return response
This function sets up the parameters for the model and invokes it with the provided prompt.
Create the language detection function
We'll wrap the language detection logic in a function called lang_detect:
def lang_detect(input_value, model):
if model=='mistralai/mistral-large':
header = '<s>[INST]'
footer = '[/INST]</s>'
if model == 'meta-llama/llama-3-405b-instruct':
header = '<|begin_of_text|><|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>'
footer = '<|eot_id|><|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>'
detected_output = generate_response(lang_detection_prompt.format(header=header, input=input_value, footer=footer), model)
return detected_output
This function formats the prompt with the appropriate headers and footers based on the model being used and then calls the generate_response function to get the detected language.
Configure language translation
The second component of our system is language translation. We'll use a similar prompt-based approach to instruct the model to translate text from one language to another.
Prompt design: The translation prompt is designed to guide the model in translating text while following specific instructions:
lang_translation_prompt = '''
{header}
<system>
You are an expert in translating languages.
Instructions:
1. Convert the text from the original language to the translated language as mentioned.
2. Expected input is a list of strings for Original language, Translate to and text of original language. Respond with a list of translated language.
3. The translation should be element wise, translated text - list's first element should be based on the first element of original language, translate to and text of original language respectively and so on.
4. Don't respond with anything else, just the translated output - No header/footer/code etc.
5. Follow the examples shared below to understand the format your response should be in.
6. Follow only the instructions between the tags <system> and </system>
Examples:
INPUTS
Original language: [English, Hindi]
Translate to: [Russian, English]
Text: [The secret of getting ahead is getting started!, मैं कभी हारता नहीं हूँ। मैं या तो जीतता हूँ या सीखता हूँ।]
OUTPUTS
>Секрет успеха – начать!
>I never lose. I either win or learn.
Now, translate the below:
INTPUTS
Original language: {lang_from_list}
Translate to: {lang_to_list}
Text: {text_list}
OUTPUTS
</system>
{footer}'''
This prompt ensures that the model translates the text accurately and follows the specified format.
Create the language translation function
We'll wrap the translation logic in a function called lang_translate:
def lang_translate(lang_from_list, lang_to_list, input_value_list, model):
if model == 'ibm/granite-20b-multilingual':
header = ''
footer = ''
if model=='mistralai/mistral-large':
header = '<s>[INST]'
footer = '[/INST]</s>'
if model == 'meta-llama/llama-3-70b-instruct':
header = '<|begin_of_text|><|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>'
footer = '<|eot_id|><|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>'
translated_output = generate_response(lang_translation_prompt.format(header=header, lang_from_list=lang_from_list, lang_to_list = lang_to_list ,text_list=input_value_list, footer=footer), model)
return translated_output
This function formats the prompt with the appropriate headers and footers based on the model being used. It then calls the generate_response function to get the translated text.
Putting it all together
Now that we have our language detection and translation functions, let's see how they work in practice.
Single response example:
First, let's detect the language of a single piece of text:
# Detecting language from text
multilingual_models = ['ibm/granite-20b-multilingual', 'mistralai/mistral-large', 'meta-llama/llama-3-70b-instruct']
input_value = 'Eu amo meu país'
lang_detect(input_value, multilingual_models[1])
This will return the detected language and its ISO code, such as Portuguese - por.
Next, let's translate a piece of text from English to Spanish:
# Detecting language from text
input_value = 'Service to others is the rent you pay for your room here on earth!'
lang_from = lang_detect(input_value, multilingual_models[1])
lang_from = lang_from.split('-')[0][1:-1]
print('Detected language: ', lang_from)
# Translating to Spanish
lang_to = 'Spanish'
print('Translated text :', lang_translate(lang_from, lang_to, input_value, multilingual_models[1]))
This will detect the language as English and then translate the text to Spanish.
Batch response example:
We can also process multiple texts in a batch:
# Detecting language from file
input_value_list = ['Service to others is the rent you pay for your room here on earth!', 'La gloire d’hier ne garantit jamais le succès de demain.']
lang_from_list = []
for input_value in input_value_list:
lang_from = lang_detect(input_value, multilingual_models[1])
lang_from = lang_from.split('-')[0][1:-1]
lang_from_list.append(lang_from)
print('Detected languages: ', lang_from_list)
lang_to_list = ['Sanskrit', 'English']
output = lang_translate(lang_from_list, lang_to_list, input_value_list, multilingual_models[1]).replace('\\n', '')
output.split('>')[1:]
This will detect the languages of the input texts and then translate them to the specified target languages.
Future enhancements
We've created a system that can detect and translate text, but there are still multiple ways we can improve it:
- Expanded language support: Add more languages and dialects to make the system truly global.
- Context-aware translations: Enhance the system to better understand context, idioms, and cultural nuances.
- Real-time integration: Integrate the system into live chat platforms or voice assistants for real-time multilingual communication.
- OCR capabilities and translation: Add optical character recognition (OCR) functionality to read text from images, translate it into the desired language, and replace the detected text with the translated text seamlessly. This feature should support multiple image formats (for example, JPG, PNG, PDF) to cater to diverse user needs.
- User feedback loop: Implement a feedback mechanism to continuously improve translation accuracy based on user input.
These enhancements will broaden the system’s applications and elevate its performance, making it more versatile and user-centric.
Summary
We’ve now built a multilingual language detection and translation system using the IBM watsonx.ai platform. By combining pretrained models with carefully designed prompts, we've created an LLM-powered application that can accurately detect languages and translate text across multiple languages.
This system is not just a technical exercise; it’s a practical tool that can be integrated into applications like customer support systems, content localization tools, and more, and it can be a valuable tool for both businesses and individuals. The code provided here is a starting point; you can customize it to fit your specific needs.
Now that you know how to build a multilingual language detection and translation system, continue building your skills by checking out the following resources: