About cookies on this site Our websites require some cookies to function properly (required). In addition, other cookies may be used with your consent to analyze site usage, improve the user experience and for advertising. For more information, please review your options. By visiting our website, you agree to our processing of information as described in IBM’sprivacy statement. To provide a smooth navigation, your cookie preferences will be shared across the IBM web domains listed here.
Tutorial
Integrate Turbonomic actions with existing automation tools
Integrate IBM Turbonomic with existing infrastructure as code (IAC) automation platforms like Terraform or Ansible for Turbonomic action execution
IBM Turbonomic is an application resource management (ARM) solution that provides full-stack visualization of your application and infrastructure stack and provides AI-powered automation to assure application performance with optimized infrastructure and lowest cost. Turbonomic provides automated action execution across the target infrastructure to optimize the infrastructure. However, organizations might also have their own automation strategy for infrastructure management using tools like Terraform or Ansible. In such situations, organizations need to look for ways to integrate and execute Turbonomic actions via their existing automation tools. This integration will ensure a single source for automation across a hybrid cloud infrastructure.
In this tutorial, we will explain how to integrate Turbonomic with existing automation tools for action orchestration.
Turbonomic Action Orchestration specifies whether Turbonomic will execute an action itself or it will pass the action request on to an orchestrator or to an action script to execute the action. Action scripts provide a script interface to introduce custom processing to Turbonomic actions. The custom scripts execute on a remote server (also called Action Script Server) that needs to be configured as a Turbonomic target as shown in the following figure.
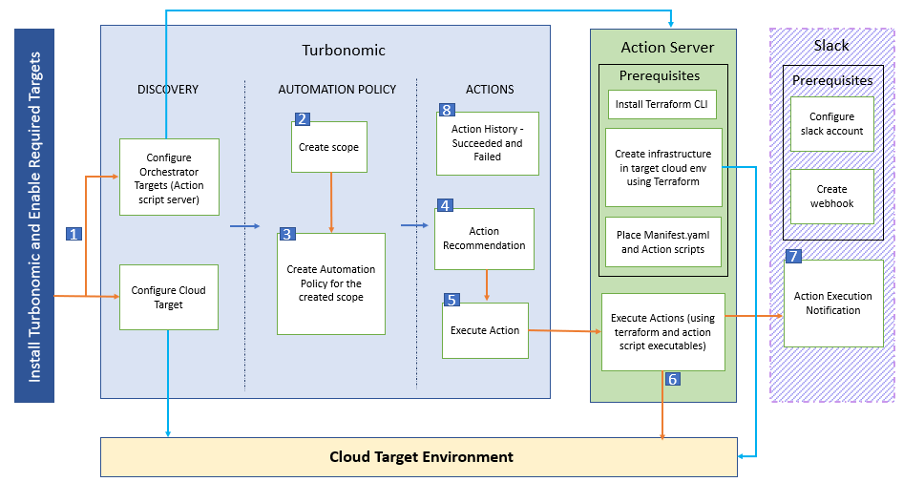
High level steps in this configuration:
- Enable and configure a target for public cloud (in this example, AWS Cloud) and an orchestrator in Turbonomic.
- Define the scope for an automation policy in Turbonomic.
- Create an automation policy for the scope defined in step 2. Define the action types and actions to be executed in pre, post and action execution phases. Optionally, define a schedule to execute the policy.
- Turbonomic recommends actions for the scoped resources.
- Turbonomic automation policy invokes the Action Script Server for action execution.
- The action is executed via the Action Script Server using Terraform.
- If a Slack webhook is enabled, then a slack notification is sent after the action is executed.
For this tutorial, we will show you how to execute Turbonomic actions using Terraform automation for the AWS infrastructure which is integrated as a target in Turbonomic for continuous optimization. As an example, we will show how a VM instance is resized in the target AWS infrastructure.
Prerequisites
- Turbonomic is deployed successfully. Refer to the documentation for setting up Turbonomic on a Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- A VM instance created on an AWS infrastructure which is added as a Public Cloud target in Turbonomic.
- Turbonomic can discover the AWS infrastructure and generate actions to optimize the infrastructure. Refer to this IBM Developer tutorial for how to set up an AWS cloud target.
- A VM with the Terraform CLI installed, which will be used as the Action Script Server.
- (Optional) A Slack account. Follow the documentation to create a webhook for receiving notifications on Slack channel.
Steps
- Step 1: Enable the Action Script target in Turbonomic
- Step 2: Set up the Action Script
- Step 3: Configure the Action Script Server as a target in Turbonomic
- Step 4: Create an Automation Policy
- Step 5: Watch the actions execute
Step 1: Enable the Action Script target in Turbonomic
Turbonomic uses a remote server called the Action Script Server to manage and execute action scripts.
To configure Action Script Server, first you need to enable Action Script Target from the Turbonomic Xl release.
Log in to the OpenShift console. go to Operators > Installed Operators > Turbonomic Platform Operator > Turbonomic Platform Operator in the turbonomic namespace.
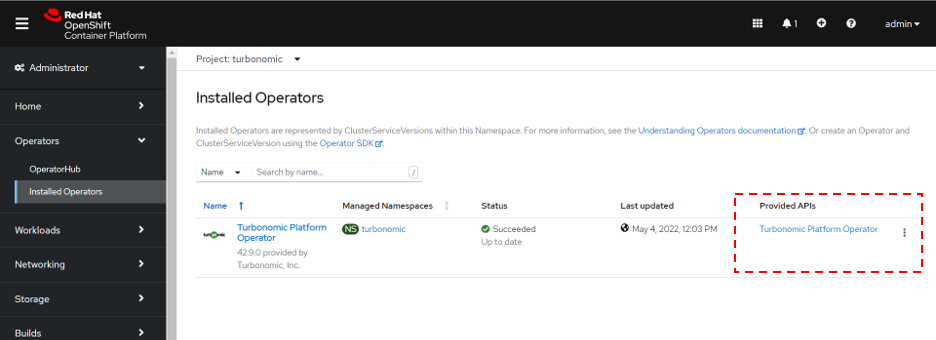
On the Turbonomic Platform Operator tab, click xl-release.

From the Actions drop-down, select Edit Xl.

On the YAML tab, add the following text in the spec section:
actionscript:
enabled: true
Then, click Save.

Step 2: Set up the Action Script
This tutorial uses a VM with automation platform tools like Terraform already configured as the Action Script Server.
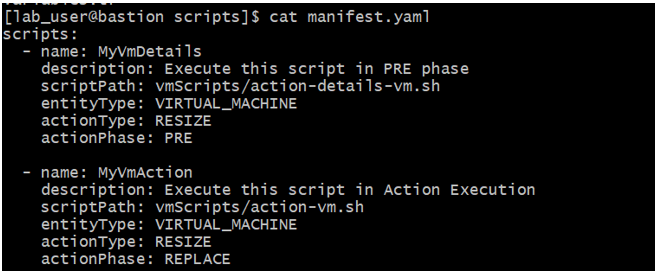
The Action Script manifest identifies the scripts that you want to expose to Turbonomic. The manifest is a file that declares an array of Script Objects for each script you want to expose. You can create the manifest as either a JSON file or a YAML file.
The following figure shows an example of a manifest file for a resize action in YAML file format:
The following figure shows an example of a manifest file for a resize action in JSON file format:
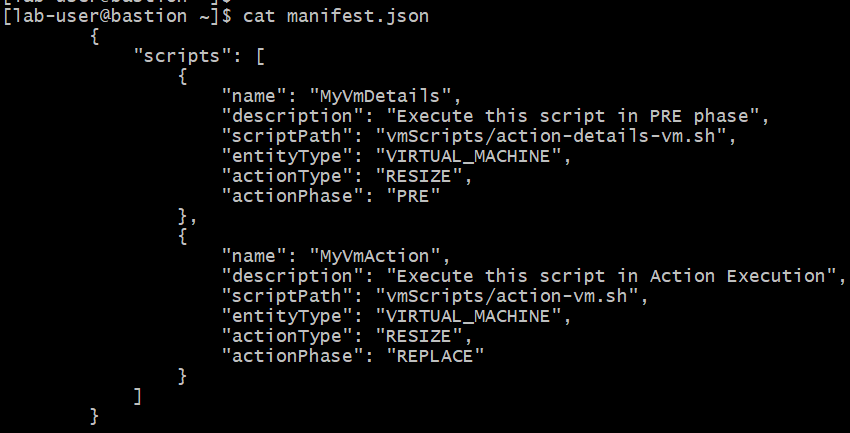
In the manifest, “scripts” is the object that contains list of scripts to be executed. For each script, you must define these properties:
- name: The name of the action script.
- description: The description of the script.
- scriptPath: The relative path to the script.
- entityType: The entity for which the action is required, such as VM or storage.
- actionType: The type of action to be executed, such as resize or suspend.
- actionPhase: The action lifecycle, such as PRE, REPLACE, or POST.
You can save the Scripts Manifest file to any location on your server. This path will be provided as the SCRIPT PATH in the Action Script target configuration (which we discuss in a later step).
The Action User (also used by Turbonomic for SSH connectivity to the Action Server) should have access to the SCRIPT_PATH and should have read and execute privileges. Also, it should be the only user with authorized access to Action Script Server’s public and private keys i.e. the key files should have 600 permission.
Now, you need to create the action scripts that you have defined in the manifest file. Place your scripts in the scriptPath provided in the manifest file and assign read and execute permissions for the Action User.
The following snippet is a sample action script for a VM resize action:
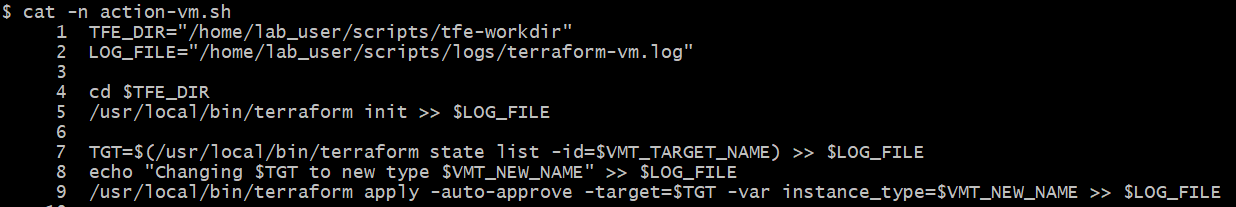
At line 5, the script is performing the terraform init command to initialize the terraform working dir. At lines 7-9, the script is reading the existing state of the target VM from Terraform state and using the “terraform apply” command to modify the instance_type of the target VM. The new instance_type is provided using -var argument through a Terraform command at line 9.
To pass general information into the action scripts, Turbonomic sets environment variables on the Action Script Server. So, these variables can be referenced in action scripts to read the action data and execute actions accordingly. In the above case, the target resource ( our VM) is referenced using VMT_NEW_NAME. For more details on action script environment variables please refer to the Turbonomic documentation.
Step 3: Configure the action Script Server as a target in Turbonomic
Now that our Action Script Server is ready, we can integrate it as target in Turbonomic. Then, Turbonomic will be able to connect to the Action Script Server over SSH and discover the manifest.yaml.
Navigate to Settings > Target Configuration > New Target > Choose Target Category as Orchestrator > Action Script.
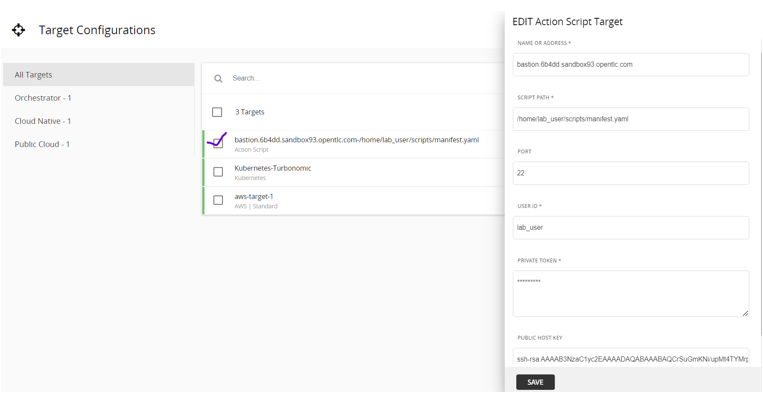
Complete these fields:
- Name or Address: The action server details.
- Script Path: The absolute path to the manifest file on the action server.
- Port: Specify port 22 for SSH connectivity.
- User ID: Turbonomic uses this user to connect to the action server over SSH. This is also used to execute the action scripts.
- Private token: The private key copied from the action server
.sshdirectory. - Public host key: The public key copied from the action server
.sshdirectory.
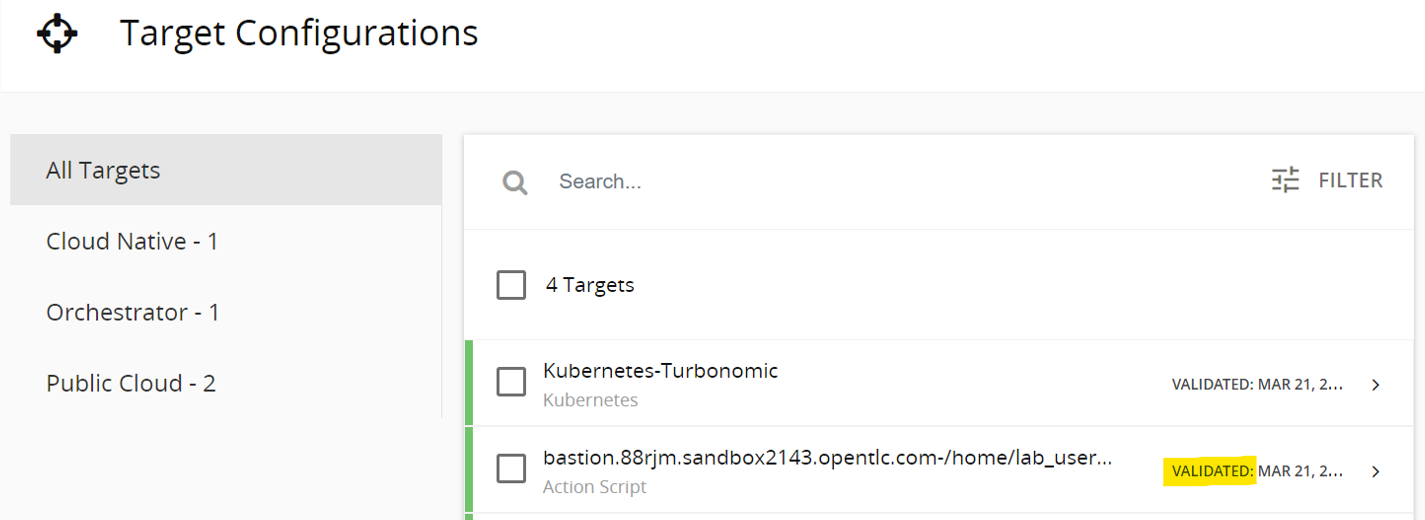
Once all the details are provided in the Action Script Target configuration page, click SAVE, and check that the target status is “Validated.”
Step 4: Create Automation Policy
Now, let’s create a VM automation policy to automatically execute a scaling action for a group of VMs via the Action script. The policy will trigger action scripts configured in the Action Script Server in the BEFORE and ACTION execution phases and optionally trigger a webhook (if Slack integration is configured) in the AFTER execution phase to send notifications to Slack.
First, we need to create a VM group to define the scope of VMs to which the policy will be applied. go to Settings > groups > Create a new group, and then change Type to Static to select the VM. Then, click Save.

Next, you need to create an automation policy.
From the left panel, click Settings and then click Policies.

On the Policy Management page that opens, click the New Automation Policy button. In the panel that opens on the right, select Virtual Machine as the policy type.
The Configure Virtual Machine Policy page opens.

Complete these fields:
- Name: The policy name.
- Scope: The scope of the policy that was created in the previous step.
- Policy Schedule: The schedule to run the policy (optional).
- Automation and Orchestration: Define how the actions are executed.
- Action Constraints: The constraints to run the actions (optional).
The Automation and Orchestration tab expands to the following page.
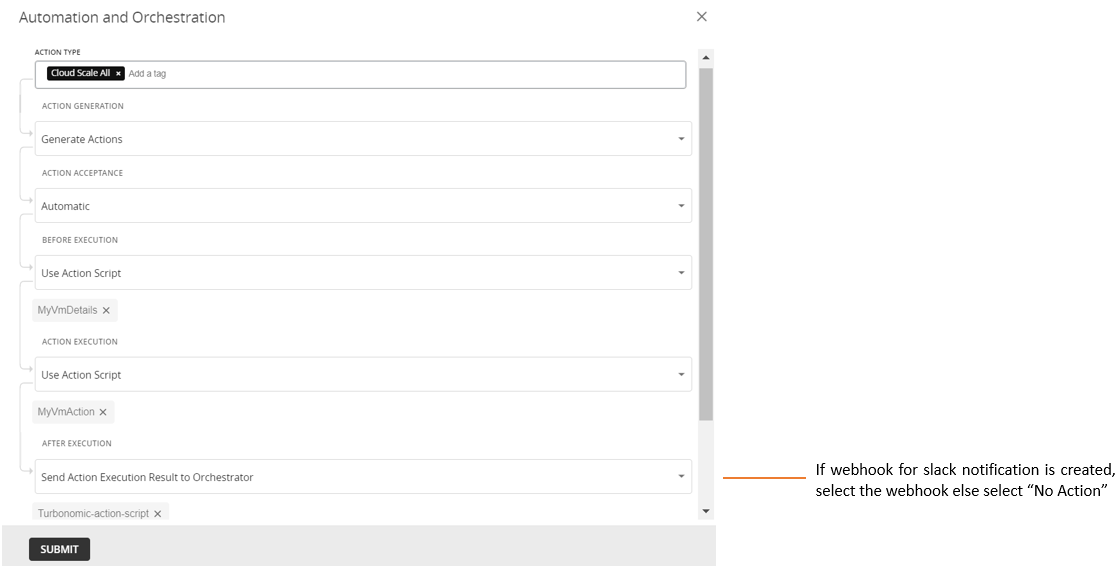
Provide the action script details for each action phase:
- Action Type: Select Cloud Scale All (as this is a RESIZE action).
- Action generation: Select generate Actions.
- Action Acceptance: Select Automatic.
- Before Execution: Select Use Action Script and select the PRE phase script name from the drop-down menu.
- Action Execution: Select Use Action Script and select the ACTION EXECUTION phase script name from the drop-down menu.
- After Execution: Select Send Action Execution Result to Orchestrator if a Slack webhook is configured for Post action notification. Select the webhook from the drop-down menu.
Then, click SUBMIT.
After you save these details, you come back to the policy configuration page. After providing all details, click Save Policy.
The policy might take up to 10 minutes to take effect.
Step 5: Watch the actions execute
In our setup, Turbonomic generates an action to downsize the underutilized VM (EC2 instance) from m5d.large to t3a.large. You will have to wait for Turbonomic to generate a scale action for the scoped VM.
go to Turbonomic Home page. Click Cloud > Virtual Machines. In the Supply Chain view, click Actions. You can view the pending actions from this page:
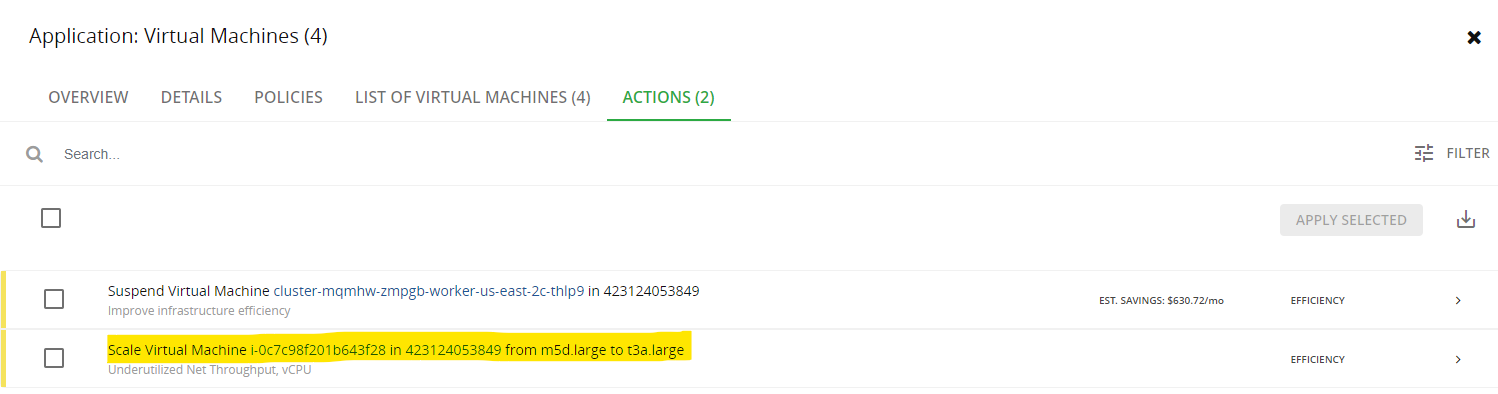
The generated action uses the VM automation policy and triggers the action script. The action scripts uses Terraform to RESIZE the VM to the new instance_type as recommended by Turbonomic. As the action is completed, it is updated in Turbonomic.
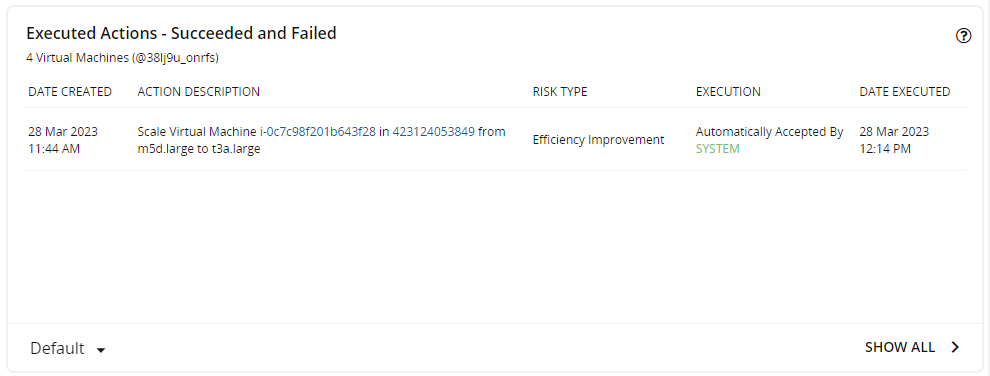
On the Turbonomic Home page, click Cloud > Virtual Machines in Supply Chain. On the Overview page, scroll down to the Executed Actions section.
This page shows the actions that have been executed on virtual machines. It shows both successful and failed actions.
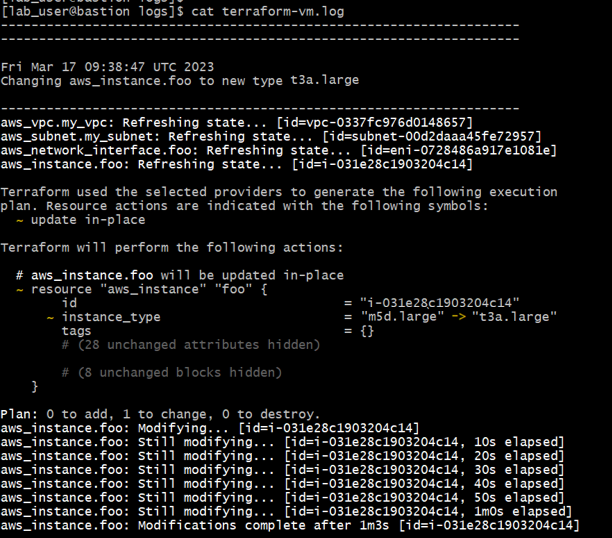
go to the Action Script Server, and then go the the ScriptPath. In the “logs” directory, you can view the Terraform logs that were generated while executing the action via Terraform. The logs show that the instance_type is modified from m5d.large to t3a.large.
You can also check the Actions for the VM is cleared after the action is executed. go to Turbonomic Home page, and click Cloud > Virtual Machines in Supply Chain. Select the Actions tab.

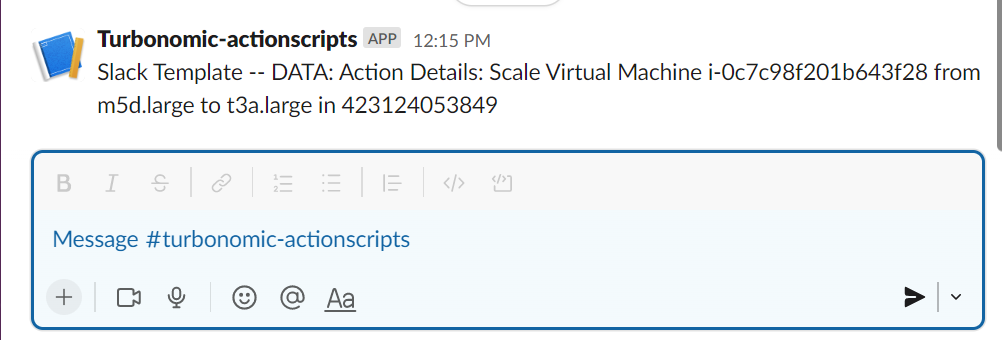
If Slack is configured and a a webhook is created, then an action execution notification is sent to Slack:
Summary and next steps
In this tutorial, we showed how you can use IAC automation tools like Terraform to take actions on Turbonomic targets using Action Scripts. Learn all about Action Orchestration in the Turbonomic documentation.
Explore more about how you can take advantage of IBM Turbonomic, by requesting a demo or trying out Turbonomic for yourself in with a Turbonomic trial. Dive into the details of the principles and operations of Turbonomic in this article, "Understanding Application Resource Management using Turbonomic".
We want to hear from you
The authors welcome your feedback on this tutorial:
- Yatin gawde -
yatin.gawde@accenture.com - Sharmistha Saha -
sharmistha.saha@accenture.com - Monica Negi -
monica.negi@accenture.com - Madhura Phatak -
madhura.m.phatak@accenture.com - Jyoti Rani -
jyotirani10@in.ibm.com