About cookies on this site Our websites require some cookies to function properly (required). In addition, other cookies may be used with your consent to analyze site usage, improve the user experience and for advertising. For more information, please review your options. By visiting our website, you agree to our processing of information as described in IBM’sprivacy statement. To provide a smooth navigation, your cookie preferences will be shared across the IBM web domains listed here.
Article
Optimizing your RAG solutions with IBM watsonx
Explore the benefits of RAG and how best to address the real-world problems, issues, and challenges
This article discusses what retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is, its challenges, and potential solutions. It also explains how IBM watsonx can help make RAG solutions better, why watsonx is important for different industries, and the benefits that watsonx brings to RAG solutions.
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is an architectural framework that combines the power of retrieval systems and large language models (LLMs) to generate accurate and contextually relevant text. In RAG, a retrieval system first fetches relevant information from a database (typically know as knowledge base), which is then used by an LLM to generate coherent and accurate responses. RAG systems aim to enhance the capabilities of LLMs by providing them with external knowledge, thereby improving the quality and reliability of the generated output.
Benefits of RAG solutions
The RAG framework has significant implications across various industries because of its ability to handle large amounts of data (that is industry owned). RAG systems improve response accuracy and provide up-to-date information.
Consider these industry use cases:
- Customer Service: Improve chatbot responses by retrieving relevant information from knowledge bases. The retrieval system pulls relevant information from the company's knowledge base (such as user manuals, FAQs, or policy documents), and the generative model uses this information to create a coherent, contextually appropriate response.
- Healthcare and Medical Assistance: Generate accurate medical reports by retrieving patient data and medical literature. The retrieval system extracts information from medical records, research papers, and health guidelines, and the generative model provides suggestions, summaries, or answers based on that information.
- Finance: Provide personalized financial advice based on the latest market data and individual portfolios.
- E-commerce: Offer accurate product recommendations and answer product-related queries.
- Education: Create intelligent tutoring systems that provide explanations and examples that are tailored to a student's understanding.
- Legal: Assist lawyers in finding relevant cases and generating briefs.
Implementing RAG solutions yields the following benefits:
- The assistance provides precise answers based on the latest information, handles a large volume of queries, and ultimately reduces the workload on human agents.
- Humans can quickly access the most relevant information, saving time for better client interactions.
- Responses are consistent with the company's policies and documentation. Responses provide the latest research findings or standards updates.
- RAG systems can offer tailored advice based on industry-specific data. By retrieving patient-specific information, the system can offer tailored advice.
RAG challenges and solutions
When implementing a RAG system, you might encounter challenges in these areas:
- Vectorization
- Retrieval
- Augmentation
- Generation
- Operational costs
The following figure illustrates the RAG solution architecture, with these challenges highlighted with a red challenge icon: ![]()
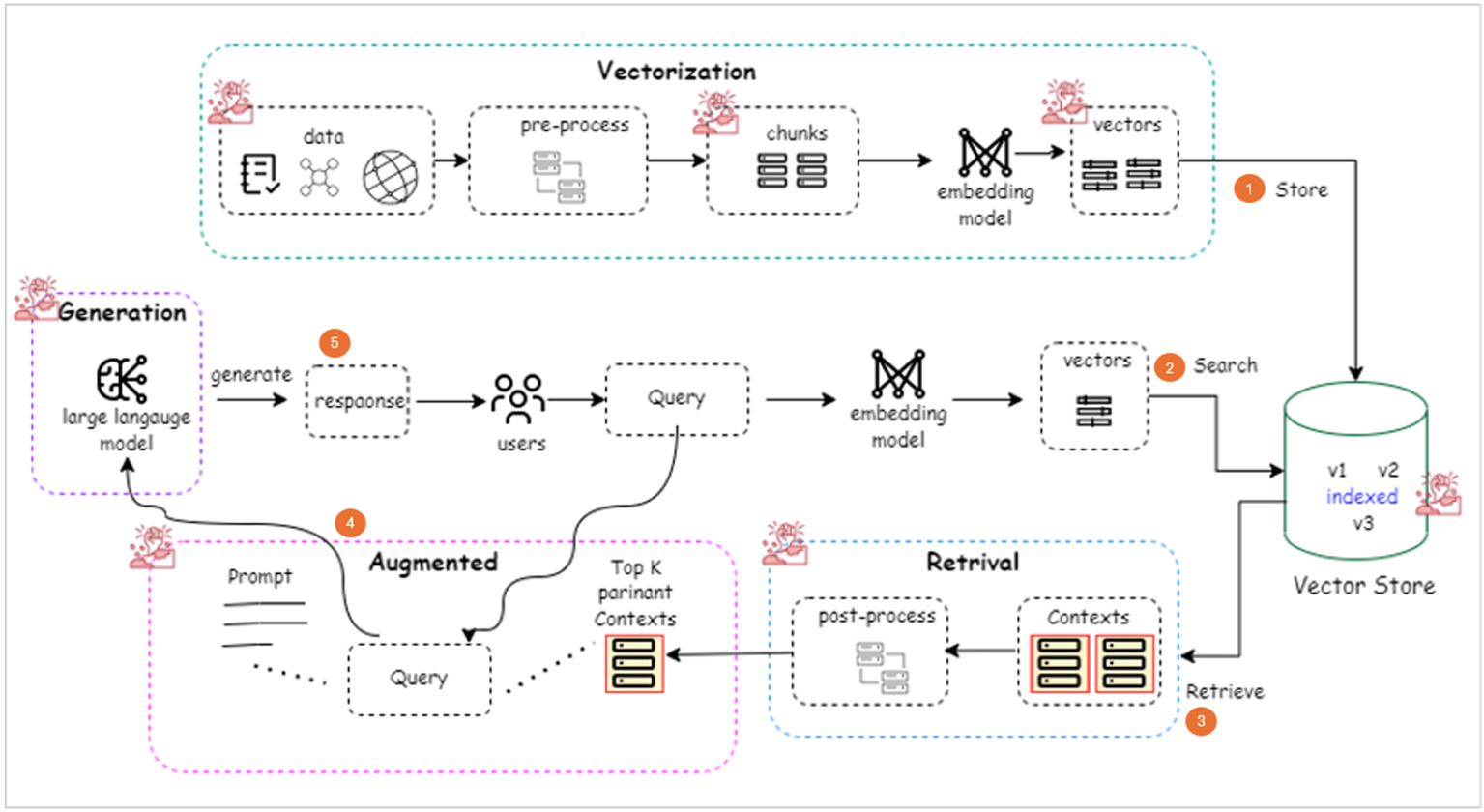
RAG challenge 1. Vectorization challenges
In RAG systems, chunking and vectorization of complex data structures from industries are interconnected processes that present several challenges, which can significantly impact the effectiveness of the solution.
Chunking involves dividing data into meaningful and manageable segments, or chunks, that retain relevant contextual information. However, with complex data structures such as nested JSON objects, nested XML, complex spreadsheet data, multi-table databases, or intricate document formats, determining the optimal chunk size and maintaining the contextual integrity of the data can be highly challenging. If chunks are too small, they may lack sufficient context, and if they are too large, they can introduce irrelevant information, both scenarios leading to suboptimal retrieval results.
Vectorization, on the other hand, is the process of converting these chunks into numerical representations, or vectors, which is the next critical step. The complexity and heterogeneity of industrial data, which can include text, images, and structured records, make vectorization particularly challenging. Choosing the right vectorization technique and ensuring it accurately captures the semantic meaning of the data is crucial. If vectorization is not done accurately (which primarily depends on correct chunking), the retrieval system might fail to fetch the most relevant information, leading to inaccurate or misleading outputs from the generative model. Additionally, the high dimensionality and sparsity of vectorized data can pose computational challenges, affecting the scalability and efficiency of the RAG system.
These challenges, if not properly addressed, can negatively impact the accuracy, contextual relevance, and performance of the RAG solution. Ineffective chunking can result in the loss of important context, while poor vectorization can lead to inaccurate retrieval, both of which degrade the quality of the generated responses. Therefore, optimizing both chunking and vectorization processes is essential for ensuring that the RAG system provides valuable and reliable outputs in real-world applications.
Additionally, flawed embeddings can hinder query disambiguation, resulting in more frequent retrieval errors and inaccurate outputs. At times, substandard embeddings may elevate the risk of the generation model producing irrelevant or erroneous information, known as hallucinations. Furthermore, inefficient embeddings can intensify computational demands and latency, slowing down the system and compromising its scalability.
Solutions for vectorization challenges
Addressing the challenges of chunking and vectorization in RAG systems requires a combination of advanced techniques and best practices.
Consider these solutions:
- Use natural language processing (NLP) to divide text into parts like paragraphs, sentences, or topics to keep the meaning clear.
- For structured data like nested JSON or multi-table databases, create a system that keeps the connections between different data levels.
- Use algorithms that change chunk sizes based on how complex the data is, helping to balance detail and context.
- Overlap chunks to make sure important information isn't lost at the edges, keeping the flow and relevance.
- Use semantic chunking for better accuracy with embedding-based searches. Models like BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) or RoBERTa can capture complex meanings in text.
- For different data types like text, images, and structured data, use techniques that represent all data in a single vector space.
- Apply principal component analysis (PCA) to reduce vector size while keeping most of the important information, which will make calculations faster.
- Use methods like t-SNE (t-distributed Stochastic Neighbour Embedding) or UMAP (Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection) to visualize high-dimensional data in lower dimensions, helping to understand and improve the vectorization process.
- Combine traditional and advanced vectorization techniques for different data types, like TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) for structured data and BERT embeddings for text.
- Make sure the chunking and user query use the same language model to avoid inaccurate results.
- For better embeddings, use contrastive learning and fine-tune models like BERT on specific data to improve embedding quality.
Consider these best practices:
- The relevance and accuracy of the generated output heavily depend on the chunks of data retrieved by the system. Retrieving the most relevant and reliable chunks ensures that the generated output is correct and useful.
- Processing large amounts of data can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. By breaking down data into smaller chunks, the system can process information more efficiently and deliver results swiftly.
- Chunks of data also provide the necessary context for the generation process. Moreover, retrieving diverse chunks from different sources helps ensure that the generated output is well-rounded.
- RAG frameworks are designed to handle large-scale tasks beyond traditional generation systems' capabilities. The use of chunks allows the system to scale up and manage larger, more complex tasks.
- Semantic-based chunking is particularly important because it ensures that chunks are meaningful and contextually relevant. This is vital for the accuracy and coherence of the generated text. Unlike normal chunking, semantic-based chunking focuses on preserving the context and semantic meaning of the data.
IBM watsonx capabilities that address vectorization challenges
The IBM watsonx portfolio offers a suite of advanced AI capabilities that can be leveraged to address the challenges of chunking and vectorization in RAG solutions.
Here's how you can use watsonx to implement the vectorization solutions:
Chunking
- Watson Discovery can be used to ingest and analyze the financial documents and market data. Watson Discovery's advanced NLP capabilities are employed to segment the text into meaningful chunks based on topics, such as investment strategies, market trends, and customer profiles. This ensures that each chunk retains relevant contextual information.
- For customer records, Watson Knowledge Studio can be used to create custom annotators that can handle structured data. These annotators help in chunking the data into manageable segments that include customer demographics, transaction history, and investment preferences.
Vectorization
- watsonx.ai and its embeddings model are used to convert the textual data from financial documents and market reports into high-dimensional vectors. These embeddings capture the semantic meaning of the text, enabling accurate retrieval.
- For structured data like customer records, Watson Machine Learning can be used to train custom embedding models. These models transform the structured data into vectors that can be used alongside the textual data vectors.
- To handle the high dimensionality of the vectors, Watson Studio can be used to apply dimensionality reduction techniques like PCA. This reduces the computational complexity while retaining the essential information.
RAG challenge 2. Retrieval challenges
In RAG systems, storing knowledge-based data in a vector database (vector DB) and the retrieval process present several challenges. One key issue is the dimensionality and size of the vectors, which can lead to high storage requirements and increased computational costs. Additionally, maintaining the freshness and relevance of the knowledge base is crucial, as outdated information can degrade the quality of generated responses.
The retrieval part faces several challenges that significantly impact the overall solution's effectiveness. Key challenges include dealing with vast amounts of data, ensuring the retrieval of relevant information, ensuring the retrieved chunks are relevant to the user query and maintaining efficiency.
The retrieval model must accurately understand and represent queries to fetch pertinent documents from a large corpus, which can be complex due to the nuances of language and context. Additionally, the retrieval process needs to be fast and scalable to handle real-time queries, which can be technically demanding.
The quality of retrieved information directly affects the generation phase, as the model relies on this data to produce coherent and accurate responses. If the retrieval is ineffective, the generated output may be irrelevant or incorrect, undermining the reliability and usefulness of the RAG solution. Therefore, optimizing the retrieval component is crucial for the success of RAG systems.
Consider a real-time customer support chatbot designed to assist users with technical issues. In this scenario, the retrieval part of the RAG solution faces significant challenges that impact the overall effectiveness:
- Create a massive and frequently updated knowledge base data after vectorization and storing them in vector DB needs significant effort including schema design, along with proper vector indexing. For example,
{"document": "<ID of the document>", "chunk_paragraph": "knowledge base chunk paragraph in text format, with metadata embedded as header or footer>", "embedding": "<vector representation of the knowledge base chunk paragraph text>" } - The chatbot needs to retrieve information from a massive and frequently updated knowledge base containing policies, product details, and promotional information. If the retrieval model struggles to keep up with the data's scale and dynamism, it might fail to fetch the latest return policy, leading to inaccurate responses.
- The customer's question combines multiple conditions (electronic items, holiday sale, and return policy, for example). The retrieval model must understand and represent this complex query effectively. If it focuses on the wrong aspects (such as prioritizing 'holiday sale' over 'return policy'), it might retrieve irrelevant information, causing the generation model to produce unhelpful responses.
- The retrieval model should understand that the query relates to the customer's role and the platform's policies, not general knowledge. If it lacks this contextual awareness, it might retrieve generic information about return policies from the web, leading to incorrect responses.
- During peak hours, such as Black Friday sales, the chatbot might need to handle thousands of queries simultaneously. If the retrieval process is not optimized for speed and scalability, it could lead to delays in response generation, frustrating customers and potentially causing the system to crash.
- If the retrieval model is unsure about which documents are most relevant (for example, there are multiple return policies for different types of electronic items), the generation model may produce vague or confusing responses, leading to a poor user experience.
Solutions for retrieval challenges
Addressing the challenges of storing vector data and retrieval in RAG systems requires a multi-faceted approach that leverages advanced techniques and best practices. Here are some key strategies to consider:
- Use techniques like PCA, t-SNE, or autoencoders to reduce the size of vectors. This makes storing and retrieving them more efficient without losing much quality.
- Implement advanced indexing methods such as Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) search algorithms, like HNSW or Annoy, to speed up the retrieval process. These methods allow for quick, approximate searches that are often good enough for many uses.
- Spread the vector data across multiple nodes or parts to manage large datasets better. This not only helps with scaling but also improves retrieval speed by searching in parallel.
- Enhance the initial query with related terms or concepts to improve retrieval accuracy. Techniques like query expansion using synonyms, related terms, or contextual information can help find more relevant vectors.
- After the initial retrieval, use a re-ranking algorithm to refine the results. This involves using more advanced models to reorder the retrieved vectors based on their relevance to the query, improving the overall quality of the retrieved information.
- Combine traditional keyword-based retrieval methods with vector-based retrieval to use the strengths of both approaches. This hybrid model can make the retrieval process more robust and accurate.
- Implement vector caching mechanisms for frequently accessed vectors and pre-fetch related data to reduce latency and improve the system's overall performance.
Consider these best practices:
- To optimize retrieval, begin by dividing each document into smaller sections, a process known as chunking. Next, employ an embedding model to transform each chunk into a vector, also referred to as an embedding vector.
- Each embedding vector and its corresponding chunk should then be stored in a Mongo vector database. Ensure that each chunk is appropriately labelled with header-footer metadata for easier identification.
- Upon receiving a user query, convert it into an embedding vector using the same embedding model. Then, search the vector database for the most similar or closest vectors to the query vector and retrieve the corresponding text chunks.
- To enhance accuracy, re-rank the retrieved search results.
IBM watsonx capabilities that address retrieval challenges
To implement the described RAG system using IBM watsonx portfolio capabilities, you can leverage various features from watsonx.data for data management and watsonx.ai for AI functionalities. Here's how you can address each strategy using IBM watsonx:
IBM watsonx.data
- IBM watsonx.data offers a vector database service named IBM watsonx.data Vector Store, designed for efficient storage and retrieval of vector data, where your optimized vector data (after dimensionality reduction) can be stored.
- IBM watsonx.data Vector Store supports advanced indexing structures like HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World) for approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) search. For example, when creating a collection in watsonx.data Vector Store, specify the index type as HNSW to enable fast, approximate searches.
- IBM watsonx.data Vector Store is designed to handle large data sets and can be deployed in a distributed manner across multiple nodes. For example, when setting up watsonx.data Vector Store, configure it to use multiple nodes or shards to distribute your vector data and enable parallel search.
- IBM watsonx.data provides caching mechanisms to improve performance. For example, configure watsonx.data Vector Store to cache frequently accessed vectors and pre-fetch related data to reduce latency and improve overall system performance.
- IBM watsonx.data supports both keyword-based and vector-based retrieval methods. Example: First, perform a keyword-based search using Watsonx.data's text search capabilities, then use the results to perform a vector-based search in watsonx.data Vector Store, combining the strengths of both approaches.
IBM watsonx.ai
- IBM watsonx.ai provides AutoAI features that can automate the application of methods like PCA or autoencoder to reduce the dimensionality of your vector data. For example, AutoAI can be used to build a model that employs PCA for dimensionality reduction, then it can be deployed as a microservice to preprocess your vector data.
- IBM watsonx.ai offers embedding models to create the vector of the query to search in vector DB and also natural language understanding (NLU) capabilities that can help enhance the initial query with related terms or concepts.
- IBM watsonx.ai offers re-ranking models to refine the results retrieved from watsonx.data Vector Store.
RAG challenge 3. Augmentation
The augmented part of the RAG framework is intricately linked to the retrieval part, and its challenges and impacts are significantly influenced by retrieval.
If the retrieval part fails to provide high-quality, relevant data, the augmented part will struggle to generate accurate and meaningful outputs. Scalability issues in the retrieval part can lead to inefficiencies in data handling, affecting the augmented part's ability to process large datasets. Latency in retrieval can delay the generation process, which is particularly problematic in real-time applications. Additionally, the complexity of integrating the retrieval system with the generation model can introduce further challenges, as any misalignment can lead to suboptimal performance. Therefore, the effectiveness of the retrieval part is critical to the overall success and impact of the augmented part in RAG solutions.
So, in summary, retrieved data quality, relevance, scalability, latency, and integration complexity issues can impact the overall effectiveness and efficiency of RAG solutions.
Solutions for augmentation challenges
To tackle the augmentation challenges in RAG systems, a thorough approach is needed.
- You can create strong data cleaning processes to remove noise, duplicates, and irrelevant information, ensuring good data quality.
- Use both automated and manual checks to confirm the accuracy and relevance of the data retrieved.
- Enhance the data set with extra metadata or contextual information to make it more relevant. For example, if the data is from a job portal, candidate CVs should have metadata managed properly in a vector DB.
- Use advanced indexing methods like inverted indexes, B-trees, or vector-based indexing to speed up data retrieval and manage scalability and latency.
- Always implement algorithms like HNSW or Faiss for faster retrieval in large datasets.
- Use distributed computing to handle large-scale data retrieval efficiently.
- Design clear prompts, preferably using Chain of Thought (CoT), to guide the generation model in using the retrieved data effectively.
- Ensure the retrieved data is relevant to the task by using context-aware retrieval methods.
- Implement feedback mechanisms to improve prompts and retrieval strategies based on the model's performance.
- Use the same embedding model for both vectorization and retrieval to ensure better alignment and coherence, avoiding misalignment between retrieval and generation models.
- Optimize the entire RAG pipeline end-to-end to minimize integration issues.
- Use hybrid models that combine retrieval and generation within a single architecture.
- Implement caching to store frequently retrieved data and reduce latency.
- Use load balancing to distribute tasks across multiple servers and leverage parallel processing to handle multiple tasks concurrently.
IBM watsonx capabilities that address augmentation challenges
- IBM watsonx data refinery can be used to build pipelines for cleaning data. For example, for a recruitment data set, use the Duplicate detection and Data profiling features to remove duplicates and irrelevant information and the Data quality feature to handle missing or inconsistent data.
- IBM watsonx.ai anomaly detection can be used to identify outliers or incorrect data. For example, automatically flag candidates with unusually high or low salaries and manually review these cases.
- IBM watsonx.data supports various indexing techniques. A Vector search feature with ANN algorithms like HNSW for faster retrieval using vector-based indexing. For example, index candidates' skill sets using vector-based indexing to improve retrieval speed for job matching.
- IBM watsonx.ai prompt lab can be used to design effective prompts. For example, craft prompts like "Given a context and background of the company job portal
{background}answer the following query from the references{retrieved and refined results from vector DB with guardrail like “while responding please ensure some instructions and guideline”: Query - “Generate a job description for a {job role} in the {industry} requiring {skills}". - IBM watsonx.ai's embedding models can be used for both vectorization data and retrieval, ensuring alignment with the generation LLM. Example: Use the same embedding model to vectorize candidate profiles and job descriptions for better matching.
RAG challenge 4. Generation challenges
In RAG systems, the generation part faces several challenges.
One key challenge is effectively utilizing the retrieved information in prompt building to generate text in a smooth and coherent manner. Another significant issue is the potential for the model to generate false or irrelevant information, a problem often referred to as "hallucinations."
Ensuring the generated text is faithful to the retrieved information is also a critical challenge. Moreover, the model must be adaptable enough to handle diverse retrieval results and weave them into a coherent narrative.
Lastly, evaluating the accuracy and relevance of the generated text automatically poses a substantial challenge, as traditional metrics may not capture the nuances of these aspects effectively. The difficulty of automatically evaluating the accuracy and relevance of generated text.
Solutions for generation challenges
Here are some ways to tackle problems in text generation within RAG systems using advanced methods and best practices.
- Use predefined templates to blend retrieved information into prompts, making sure the generated text is smooth and coherent.
- Include CoT prompting, which adds intermediate reasoning steps to guide the model in using retrieved information effectively, along with examples and hints.
- Train the model with Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) to reduce errors and make the text more accurate.
- Set up a system to filter out or correct any generated text that is wrong or irrelevant.
- Use contrastive learning to encourage the model to produce text that matches the meaning of the retrieved information.
- Adjust prompts based on the type and amount of retrieved information. Have human evaluators check the accuracy and relevance of the generated text.
- Use fact-checking tools and evaluation metrics to ensure the generated text is correct.
IBM watsonx capabilities that address generation challenges
To implement the above-described solution using IBM Watsonx platform capabilities, including Watsonx.data and Watsonx.ai, you can leverage several features and techniques.
Here's how you can address each requirement with examples:
IBM watsonx.ai prompt lab can be used to create and store predefined templates. For example, create a template like "Given the information: {retrieved_info}, generate a summary explaining the main points."
- CoT prompting in Prompt Lab can be used to design prompts that guide the model through intermediate reasoning steps. For example, "First, identify the key entities in the retrieved information: {retrieved_info}. Then, explain the relationship between these entities. Finally, generate a summary based on these relationships. Hint: Use delimiters like "Step 1: ...", "Step 2: ...", etc., to guide the model."
- Dynamic prompts can be created using Prompt Lab. For example, design prompts that change based on the type and quantity of retrieved information. If the retrieved information is a list of entities, the prompt could be "Generate a summary describing the relationships between these entities: {entities_list}."
IBM watsonx.ai
- The watsonx.ai text classification model (
flan-ul2-20b) can be used to filter factually incorrect or irrelevant text. For example, train a classifier to identify factually incorrect or irrelevant text. Use this classifier to filter out or flag such generated text. - IBM watsonx.ai can be used to create AI agents with the feedback mechanism to improve response accuracy. Also, integrate a human-in-the-loop process for human evaluation. For example, after the model generates text, send it to evaluators AI-Agent for assessment. Use it’s feedback to improve the prompting engineering.
- Leverage watsonx.ai capabilities for entity extraction and semantic similarity checks. This approach ensures that the generated text is accurate and relevant to the retrieved information.
- The watsonx.ai text classification model (
IBM watsonx.data data validation can be used to validate the generated text (using a watsonx.ai LLM) against the retrieved information (from the watsonx.data vector DB). To validate the generated text, extract key information from the retrieved data using wtsonx.ai LLM with few-shots prompting. Compare the generated text with the extracted information using methods such as keyword matching, semantic similarity (using models like BERT or Sentence Transformers), and fact checking.
RAG challenge 5. Performance overhead
RAG systems that combine retrieval mechanisms with generative models can face several challenges that contribute to performance overhead and longer response times.
Especially when dealing with large data sets, the time required to search through them increases. Additionally, more complex queries can further extend the processing time, contributing to retrieval latency. Also, larger generative models tend to take more time to produce responses.
This latency can vary based on several factors, including the type of hardware used (such as GPU vs. CPU) and the specific architecture of the model. Additionally, the process of integrating retrieval and generation components can introduce additional delays. These delays can arise from various factors, such as transferring data between different systems or handling data in different formats as it moves between the retrieval and generation components.
Solutions for performance issues
To reduce retrieval latency, you should apply indexing techniques like inverted indexes or approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) search. For generation latency, the use of smaller, distilled, or pruned models is recommended to maintain performance while decreasing inference time. Additionally, to minimize the overhead of integrating retrieval and generation, it advises streamlining the integration pipeline by eliminating unnecessary steps and enhancing data flow between components
IBM watsonx capabilities that address performance challenges
IBM watsonx portfolio can significantly help in addressing the performance overhead of RAG systems by offering advanced tools and capabilities.
- To reduce retrieval latency, the watsonx.data Vector Database can employ efficient indexing techniques such as inverted indexes or approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) search, which are optimized for quick and accurate data retrieval.
- For generation latency, the watsonx.ai Granite 3.0 high-performant models maintain high performance while decreasing inference time, ensuring faster response generation. Additionally, watsonx.ai assists in minimizing the overhead of integrating retrieval and generation components by providing streamlined integration pipelines.
- For the RAG pattern overall, watsonx.ai offers pre-configured frameworks and templates. These templates handle the basic structure of the retrieval and generation pipeline, saving developers time and effort compared to building everything from scratch. By leveraging these capabilities, watsonx.ai can substantially improve the overall performance and responsiveness of RAG systems.
RAG challenge 6. Operations and cost
RAG is a powerful technique that combines the strengths of retrieval-based and generation-based models to improve the quality and relevance of generated text. However, implementing RAG systems comes with certain operational and cost burdens.
- Gathering and maintaining a large, up-to-date corpus of documents or data that the retrieval system can draw from. And then cleaning, normalizing, and indexing the data to make it searchable and retrievable.
- Building and maintaining an efficient index for the corpus. This can be computationally intensive and requires regular updates.
- Implementing a retrieval system that can quickly and accurately retrieve relevant documents or passages based on the input query.
- Prompt based tuning or fine-tuning a generation model to work effectively with the retrieved documents.
- Integrating the retrieval and generation components into a cohesive pipeline that can handle end-to-end queries.
- Ensuring that the retrieval and generation steps are performed quickly enough to meet user expectations.
- Ensuring that the system can scale to handle a large number of queries and a growing corpus.
- Regularly updating the generation model (in case used fine-tuned model) to improve performance and adapt to new data.
- Keeping the corpus up-to-date with new information and removing outdated or irrelevant data.
- Costs associated with storing a large corpus of data (Vendor DB)
- Costs for the computational resources needed for indexing (Vector DB), retrieval, and generation (context length - token in/out processing), without normalised token. This includes CPU, GPU, and memory usage.
- Costs associated in case of fine-tuning generation FM/LLM, which can be expensive due to the need for high-performance hardware and long training times.
- Costs for the resources (data scientists and engineers) management responsible for building and maintaining the RAG system.
- Costs for ensuring the security and privacy of the data, including encryption, access controls, and compliance with regulations.
- Costs for ensuring compliance with data protection laws and industry standards.
- Cost incurs on irritant , redundant prompt with unnecessary information like stop words, punctuation , salutation during generation using LLM (optimize token)
IBM watsonx capabilities that address operations and cost challenges
Leveraging the IBM watsonx portfolio, especially IBM watsonx.ai, watsonx.data, and wastsonx governance, can help mitigate the operational and cost burdens associated with a RAG system at scale.
Here’s how the watsonx portfolio capabilities can address each of the challenges:
- The IBM watsonx portfolio, especially watsonx.ai, can significantly mitigate the operational and cost burdens associated with a RAG system at scale. By leveraging watsonx's advanced AI and machine learning tools, organizations can streamline various aspects of the RAG pipeline. For instance, watsonx can automate the gathering and maintenance of a large, up-to-date corpus of documents, utilizing its data ingestion and management capabilities to clean, normalize, and index data efficiently. This ensures that the corpus remains searchable and retrievable without extensive manual intervention.
- Also, watsonx.ai offers robust indexing solutions that can build and maintain efficient indices for the corpus, reducing the computational intensity and the need for regular updates. Its advanced retrieval systems can quickly and accurately retrieve relevant documents or passages based on input queries, enhancing the overall performance of the RAG system. Additionally, watsonx.ai provides tools for prompt-based tuning and fine-tuning generation models, ensuring they work effectively with the retrieved documents.
- Integrating the retrieval and generation components into a cohesive pipeline is simplified with the watsonx portfolio, which supports end-to-end query handling. The watsonx products ensure that retrieval and generation steps are performed swiftly to meet user expectations and can scale to handle a large number of queries and a growing corpus. Watsonx also facilitates regular updates to the generation model, improving performance and adapting to new data without significant overhead.
- In terms of cost savings, watsonx can help reduce expenses associated with storing a large corpus of data by optimizing storage solutions and leveraging cloud-based services. It minimizes computational resource costs for indexing, retrieval, and generation by utilizing efficient algorithms and scalable infrastructure. Fine-tuning generation models becomes more cost-effective with Watsonx's high-performance hardware and reduced training times.
- And, watsonx can lower the costs associated with managing data scientists and engineers by providing intuitive tools and automation features that simplify the building and maintenance of the RAG system. It also ensures the security and privacy of data through encryption, access controls, and compliance with regulations, reducing the costs associated with data protection and compliance.
- Token optimization techniques for reducing costs in implementing a RAG system is described in this article, "Token optimization: The backbone of effective prompt engineering."
IBM watsonx.governance offers these cost-saving capabilities:
- Assessing well the retrieved documents align with the user's query. This helps identify and improve the quality of the knowledge base or vector database used in the RAG system.
- Evaluating whether the generated response is grounded in the retrieved information or if it introduces hallucinations. This ensures the accuracy and reliability of the generated content.
- Measuring how relevant the generated answer is to the original query. This helps fine-tune the prompt engineering and model selection processes.
- Ongoing monitoring of the RAG system's performance, allowing for timely identification of potential issues or areas for improvement.
- By analyzing the evaluation results, you can make data-driven decisions to refine the RAG pipeline, such as adjusting the retrieval algorithm, improving the prompt engineering, or retraining the language model.
Optimized RAG Solution Architecture with IBM Watsonx footprint
Throughout this article I have outlined the challenges of implementing RAG systems, and proposed solutions to address those challenges while highlighting how the AI capabilities in the watsonx portfolio provide an optimized RAG solution.
The following figure depicts a fully optimized RAG solution architecture that uses IBM watsonx portfolio capabilities, which are highlighted by a watsonx icon: ![]()
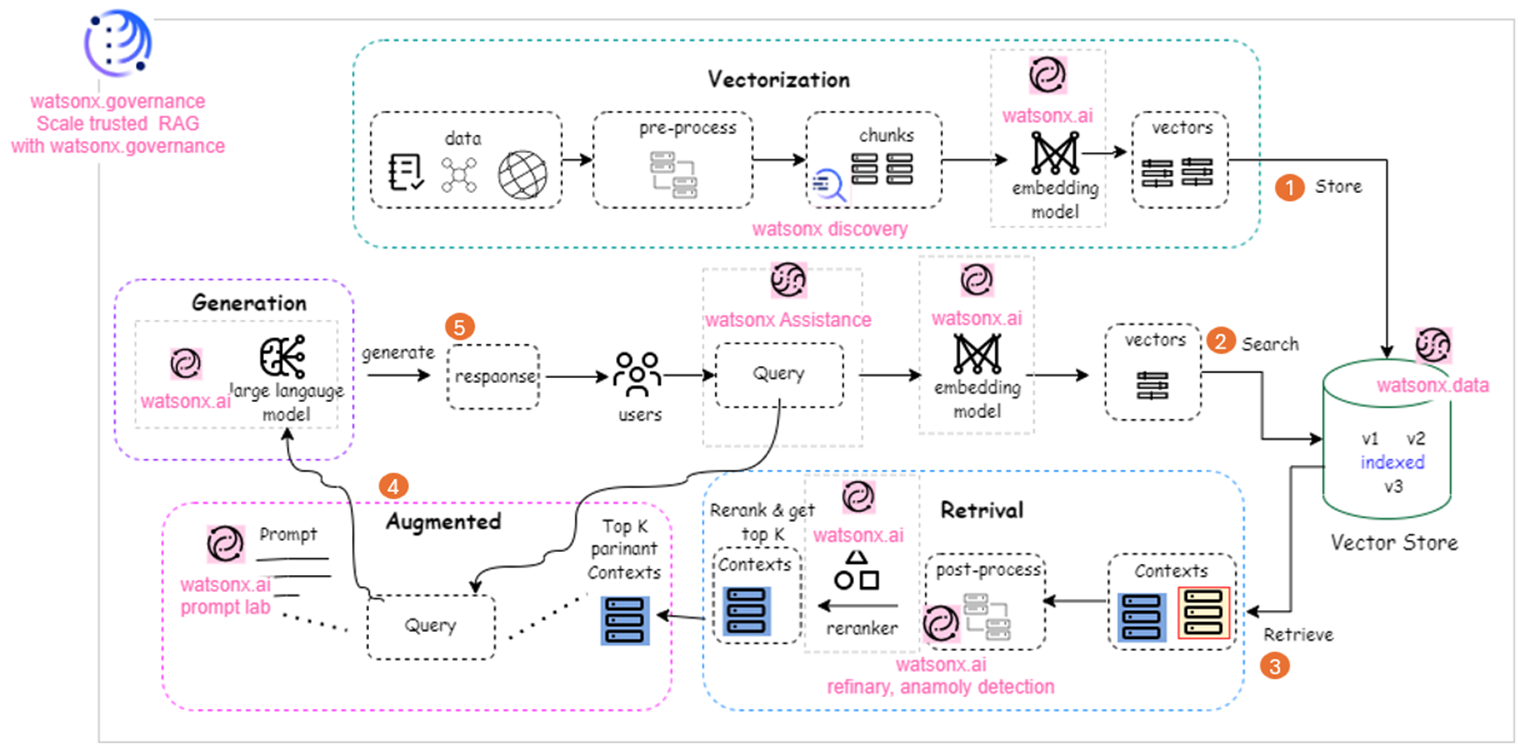
This diagram illustrates how watsonx's footprint optimizes the RAG solution by addressing the challenges presented in the previous figure at the start of this article. The key points of how the watsonx products address the key RAG challenges are enumerated in the diagram:
- Use watsonx Discovery and the watsonx.ai embedding model to preprocess, chunk, and vectorize source data, subsequently storing it in a vector database.
- Vectorize user queries using the watsonx.ai embedding model and perform searches on the watsonx.data vector database.
- Post-process the retrieved vector contexts using watsonx.ai Refinery and Anomaly Detection, followed by watsonx.ai Reranker to identify the top K relevant contexts.
- Augment the query with retrieved, refined, and reranked contexts using a strong prompt.
- Generate a response to the augmented query using the watsonx.ai LLM.
Conclusion
The article discussed the RAG solution, highlighting its importance, challenges, and optimization strategies by leveraging IBM watsonx capabilities. RAG combines retrieval systems and large language models to generate accurate and contextually relevant text by fetching relevant information from a knowledge base.
RAG solutions are beneficial across various industries, such as customer service, healthcare, finance, e-commerce, education, and legal, by providing precise, up-to-date, and consistent responses.
And yet, RAG faces several challenges, including complex data structures, vectorization, retrieval efficiency, and generation accuracy. The article suggests solutions like advanced NLP techniques, multimodal embedding, dimensionality reduction, and re-ranking algorithms to address these challenges.
The IBM watsonx portfolio offers a suite of advanced AI capabilities that can be leveraged to implement these solutions, such as watsonx-driven chunking, Watson Knowledge Studio for structured data handling, watsonx.ai embeddings for vectorization, watsonx.data Vector Database, and Watson Studio for dimensionality reduction.
Next steps
Explore the IBM RAG Cookbook, which is a comprehensive collection of best practices, considerations, and tips for building RAG solutions tailored to business applications.
And, explore the differences between RAG and fine-tuning.