About cookies on this site Our websites require some cookies to function properly (required). In addition, other cookies may be used with your consent to analyze site usage, improve the user experience and for advertising. For more information, please review your options. By visiting our website, you agree to our processing of information as described in IBM’sprivacy statement. To provide a smooth navigation, your cookie preferences will be shared across the IBM web domains listed here.
Article
Implementing NVIDIA MIG in Red Hat OpenShift to optimize GPU resources in containerized environments
A comprehensive guide for implementing NVIDIA MIG in Red Hat OpenShift
In the rapidly evolving landscape of containerized applications and cloud-native technologies, efficient resource utilization is paramount. For organizations leveraging GPU-accelerated workloads, particularly in the realms of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), optimizing GPU usage can lead to significant performance improvements and cost savings.
This comprehensive guide explores how to harness NVIDIA's Multi-Instance GPU (MIG) technology within Red Hat OpenShift to achieve unprecedented levels of GPU optimization and utilization. Learn more about optimizing GPU resources with NVIDIA MIG in this article.
GPU optimization techniques
There are two key GPU optimization techniques: the single strategy and the mixed strategy.
Single Strategy
In the single strategy technique, all MIG devices on a GPU are created with the same size. For example, on an A100-SXM4-40GB profile, you could create 7 slices of 1G.5GB or 3 slices of 2G.10GB.
Mixed Strategy
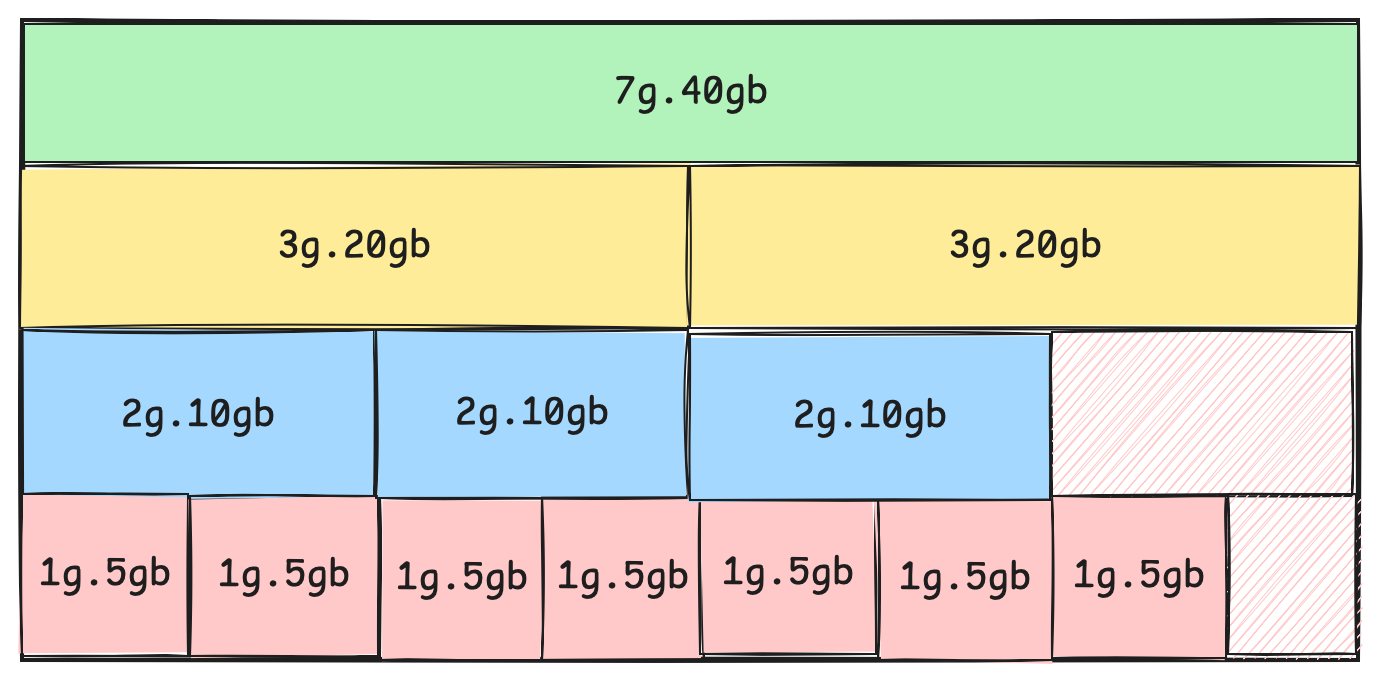
In mixed strategy technique, you create MIG devices of different sizes on the same GPU. For example, you could partition a GPU into two 1G.5GB units, one 2G.10GB unit, and one 3G.20GB unit.
Key NVIDIA MIG components used in OpenShift
To fully leverage MIG in an OpenShift environment, several key components work in concert:
- NVIDIA GPU Operator: This Kubernetes operator automates the deployment and management of GPU software components within OpenShift clusters. It handles the installation of drivers, runtime libraries, and monitoring tools necessary for GPU operations.
- NVIDIA Device Plugin: This plugin exposes GPU resources to the Kubernetes scheduler, enabling it to make informed decisions about pod placement based on available GPU resources, including MIG instances.
- NVIDIA Container Toolkit: This toolkit enables containers to access and utilize GPU capabilities, ensuring that containerized applications can leverage the full power of NVIDIA GPUs.
- NVIDIA Driver: The driver provides the essential software interface between the operating system and the GPU hardware, enabling communication and control.
Implementing MIG in Red Hat OpenShift
It really is quite simple to implement MIG in Red Hat OpenShift:
- Install the NVIDIA GPU operator.
- Configure MIG.
- Verify the MIG configuration.
Step 1. Install the NVIDIA GPU Operator
- Log into the OpenShift web console with cluster administrator privileges.
- Navigate to the Operator Hub and search for "NVIDIA GPU Operator".
- Click Install and follow the prompts to complete the installation process.
Step 2. Configure MIG
Once the GPU Operator is installed, you can configure a MIG by creating a ClusterPolicy custom resource. This resource defines the MIG strategy and configuration for your cluster.
apiVersion: nvidia.com/v1
kind: ClusterPolicy
metadata:
name: gpu-cluster-policy
spec:
mig:
strategy: mixed
config:
- gpuIds: ["0", "1"]
mig1g.5gb: 2
mig2g.10gb: 1
- gpuIds: ["2", "3"]
mig3g.20gb: 2
Apply this configuration using the OpenShift CLI:
oc apply -f clusterpolicy.yaml
Step 3. Verify the MIG configuration
After applying the configuration, verify the status of MIG devices:
oc exec -it <nvidia-device-plugin-pod> -- nvidia-smi mig -lgi
This command will display the current MIG configuration on your GPU nodes.
Optimization strategies for MIGs in OpenShift
Multi-Instance GPU (MIG) technology offers powerful optimization strategies for GPU resource allocation in OpenShift Container Platform environments.
Fine-Grained Resource Allocation
MIG allows for precise GPU resource allocation, enabling administrators to create various profiles tailored to specific workload requirements. For instance, on an NVIDIA A100-40GB GPU, you could create as shown in the mixed strategy above:
- 7 instances of 1G.5GB for lightweight inference tasks
- 3 instances of 2G.10GB for medium-sized training jobs
- 1 instance of 7G.40GB for large-scale deep learning models
This granular control ensures optimal resource utilization across diverse AI and ML workloads.
Dynamic Reconfiguration
One of the key advantages of MIG in OpenShift is the ability to dynamically reconfigure MIG geometries. This flexibility allows administrators to adapt to changing workload demands in real-time, without requiring system restarts. By monitoring workload patterns and GPU utilization, you can adjust MIG profiles to ensure optimal resource allocation at all times.
Workload-specific optimizations
Two workload-specific optimizations are encouraged:
- AI/ML pipeline optimizations
- Multi-tenant environment optimizations
AI/ML pipeline optimizations
For complex AI/ML pipelines, consider using a mix of MIG profiles to optimize each stage of the workflow:
- Use smaller instances (for example, 1G.5GB) for data preprocessing and feature engineering tasks
- Allocate medium-sized instances (for example, 2G.10GB) for model training phases
- Reserve larger instances (for example, 4G.20GB) for inference on production models
This approach maximizes GPU utilization across the entire ML lifecycle, ensuring that each stage has access to appropriate GPU resources.
Multi-tenant environment optimizations
In multi-user scenarios, MIG enables efficient resource sharing while maintaining performance isolation:
- Assign smaller MIG instances to data scientists for experimentation and development
- Provide larger instances for production workloads that require more computational power
- Use mixed configurations to support both interactive notebooks and batch jobs simultaneously
This strategy improves GPU accessibility for all users while ensuring that critical workloads have access to the necessary resources.
Performance monitoring and tuning
With MIG, these performance monitoring and tuning tasks are possible:
- GPU telemetry
- Automated scaling
GPU telemetry
You can use the NVIDIA DCGM Exporter to collect detailed GPU metrics, including:
- GPU utilization
- Memory usage
- Power consumption
- Temperature
Use this data to identify bottlenecks and optimize MIG configurations for better performance. By analyzing these metrics over time, you can make informed decisions about resource allocation and identify opportunities for further optimization.
Automated scaling
Implement auto-scaling policies based on GPU utilization metrics to ensure efficient resource allocation:
- Scale up MIG instances when utilization consistently exceeds 80%
- Scale down or reconfigure when utilization drops below 20%
This approach ensures that GPU resources are always optimally allocated, improving overall cluster efficiency and reducing costs.
Advanced MIG configurations
Finally, consider these advanced MIG configurations:
- Heterogeneous MIG setups
- Integration with OpenShift virtualization
Heterogeneous MIG setups
For maximum flexibility, consider using the 'mixed' MIG strategy, which allows for diverse MIG configurations across different GPUs:
spec:
mig:
strategy: mixed
config:
- gpuIds: ["0", "1"]
mig1g.5gb: 2
mig2g.10gb: 1
- gpuIds: ["2", "3"]
mig3g.20gb: 2
This configuration supports a wide range of workload types on a single node, providing the flexibility to run both small-scale and large-scale GPU workloads simultaneously.
Integration with OpenShift virtualization
For organizations leveraging virtualized environments, MIG can be used to provide GPU acceleration to virtual machines:
- Enable GPU passthrough in the OpenShift Virtualization operator
- Create MIG profiles suitable for VM workloads
- Assign MIG-based vGPUs to VMs for accelerated computing in virtualized environments
This integration allows for GPU acceleration in both containerized and virtualized workloads, providing a unified platform for all types of GPU-accelerated applications.
Conclusion
The integration of NVIDIA MIG technology with Red Hat OpenShift provides a powerful solution for optimizing GPU resources in containerized environments. By enabling fine-grained GPU partitioning, organizations can significantly improve resource utilization, enhance workload isolation, and maximize the value of their GPU investments.
The strategies outlined in this guide, from fine-grained resource allocation and dynamic reconfiguration to workload-specific optimizations and advanced monitoring, provide a comprehensive approach to GPU optimization in OpenShift environments. By implementing these techniques, organizations can create a highly efficient, flexible, and cost-effective platform for GPU-accelerated computing.
As AI and machine learning workloads continue to grow in importance and complexity, the combination of MIG and OpenShift offers a scalable, efficient solution that can adapt to evolving computational demands. By mastering these optimization techniques, organizations can stay at the forefront of GPU-accelerated computing, driving innovation and maintaining a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving landscape of AI and ML technologies.
Acknowledgements
This article was produced as part of an IBM Open Innovation Community Initiative.